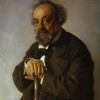Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (English: ; Russian: Александр Сергеевич Пушкин, tr. Aleksandr Sergejevich Pushkin, IPA: [ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn] (listen); 6 June [O.S. 26 May] 1799 – 10 February [O.S. 29 January] 1837) was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era who is considered by many to be the greatest Russian poet and the founder of modern Russian literature.Pushkin was born into Russian nobility in Moscow.
His father, Sergey Lvovich Pushkin, belonged to Pushkin noble families. His maternal great-grandfather was African-born general Abram Petrovich Gannibal. He published his first poem at the age of 15, and was widely recognized by the literary establishment by the time of his graduation from the Tsarskoye Selo Lyceum. Upon graduation from the Lycee, Pushkin recited his controversial poem "Ode to Liberty", one of several that led to his exile by Tsar Alexander the First. While under the strict surveillance of the Tsar's political police and unable to publish, Pushkin wrote his most famous play, the drama Boris Godunov. His novel in verse, Eugene Onegin, was serialized between 1825 and 1832.
Pushkin was fatally wounded in a duel with his brother-in-law, Georges-Charles de Heeckeren d'Anthès, also known as Dantes-Gekkern, a French officer serving with the Chevalier Guard Regiment, who attempted to seduce the poet's wife, Natalia Pushkina.
Ayn Rand (born Alisa Zinovyevna Rosenbaum; February 2 [O.S. January 20] 1905 – March 6, 1982) was a Russian-American writer and philosopher.
She is known for her two best-selling novels, The Fountainhead and Atlas Shrugged, and for developing a philosophical system she named Objectivism. Educated in Russia, she moved to the United States in 1926. She had a play produced on Broadway in 1935 and 1936. After two early novels that were initially unsuccessful, she achieved fame with her 1943 novel, The Fountainhead. In 1957, Rand published her best-known work, the novel Atlas Shrugged. Afterward, she turned to non-fiction to promote her philosophy, publishing her own periodicals and releasing several collections of essays until her death in 1982.
Rand advocated reason as the only means of acquiring knowledge and rejected faith and religion. She supported rational and ethical egoism and rejected altruism. In politics, she condemned the initiation of force as immoral and opposed collectivism and statism as well as anarchism, instead supporting laissez-faire capitalism, which she defined as the system based on recognizing individual rights, including property rights. In art, Rand promoted romantic realism. She was sharply critical of most philosophers and philosophical traditions known to her, except for Aristotle, Thomas Aquinas and classical liberals.Literary critics received Rand's fiction with mixed reviews and academia generally ignored or rejected her philosophy, though academic interest has increased in recent decades. The Objectivist movement attempts to spread her ideas, both to the public and in academic settings. She has been a significant influence among libertarians and American conservatives.
Antoine Marie Jean-Baptiste Roger, comte de Saint-Exupéry, simply known as de Saint-Exupéry (UK: , US: , French: [ɑ̃twan də sɛ̃t‿ɛɡzypeʁi]; 29 June 1900 – 31 July 1944), was a French writer, poet, aristocrat, journalist and pioneering aviator.
He became a laureate of several of France's highest literary awards and also won the United States National Book Award. He is best remembered for his novella The Little Prince (Le Petit Prince) and for his lyrical aviation writings, including Wind, Sand and Stars and Night Flight.
Saint-Exupéry was a successful commercial pilot before World War II, working airmail routes in Europe, Africa and South America. At the outbreak of war, he joined the French Air Force (Armée de l'Air), flying reconnaissance missions until France's armistice with Germany in 1940. After being demobilised from the French Air Force, he travelled to the United States to help persuade its government to enter the war against Nazi Germany. Following a 27-month hiatus in North America, during which he wrote three of his most important works, he joined the Free French Air Force in North Africa, although he was far past the maximum age for such pilots and in declining health. He disappeared and is believed to have died while on a reconnaissance mission over the Mediterranean in July 1944.
Prior to the war, Saint-Exupéry had achieved fame in France as an aviator. His literary works – among them The Little Prince, translated into 300 languages and dialects – posthumously boosted his stature to national hero status in France. He earned further widespread recognition with international translations of his other works. His 1939 philosophical memoir Terre des hommes (titled Wind, Sand and Stars in English) became the name of an international humanitarian group; it was also used to create the central theme of the most successful world's fair of the 20th century, Expo 67 in Montreal, Quebec. Saint-Exupéry's birthplace, Lyon, has also named its main airport after him.
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer.
He was lauded as the "greatest humorist this country has produced", and William Faulkner called him "the father of American literature". His novels include The Adventures of Tom Sawyer (1876) and its sequel, the Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (1884), the latter often called "The Great American Novel".
Twain was raised in Hannibal, Missouri, which later provided the setting for Tom Sawyer and Huckleberry Finn. He served an apprenticeship with a printer and then worked as a typesetter, contributing articles to the newspaper of his older brother Orion Clemens. He later became a riverboat pilot on the Mississippi River before heading west to join Orion in Nevada. He referred humorously to his lack of success at mining, turning to journalism for the Virginia City Territorial Enterprise. His humorous story, "The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County", was published in 1865, based on a story that he heard at Angels Hotel in Angels Camp, California, where he had spent some time as a miner. The short story brought international attention and was even translated into French. His wit and satire, in prose and in speech, earned praise from critics and peers, and he was a friend to presidents, artists, industrialists, and European royalty.
Twain earned a great deal of money from his writings and lectures, but he invested in ventures that lost most of it—such as the Paige Compositor, a mechanical typesetter that failed because of its complexity and imprecision. He filed for bankruptcy in the wake of these financial setbacks, but he eventually overcame his financial troubles with the help of Henry Huttleston Rogers. He eventually paid all his creditors in full, even though his bankruptcy relieved him of having to do so.
Twain was born shortly after an appearance of Halley's Comet, and he predicted that he would "go out with it" as well; he died the day after the comet returned.
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 1854 – 30 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright.
After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of London's most popular playwrights in the early 1890s. He is best remembered for his epigrams and plays, his novel The Picture of Dorian Gray, and the circumstances of his criminal conviction for "gross indecency", imprisonment, and early death at age 46.
Wilde's parents were successful Anglo-Irish intellectuals in Dublin. Their son became fluent in French and German early in life. At university, Wilde read Greats; he proved himself to be an outstanding classicist, first at Trinity College Dublin, then at Oxford. He became known for his involvement in the rising philosophy of aestheticism, led by two of his tutors, Walter Pater and John Ruskin. After university, Wilde moved to London into fashionable cultural and social circles.
As a spokesman for aestheticism, he tried his hand at various literary activities: he published a book of poems, lectured in the United States and Canada on the new "English Renaissance in Art" and interior decoration, and then returned to London where he worked prolifically as a journalist. Known for his biting wit, flamboyant dress and glittering conversational skill, Wilde became one of the best-known personalities of his day. At the turn of the 1890s, he refined his ideas about the supremacy of art in a series of dialogues and essays, and incorporated themes of decadence, duplicity, and beauty into what would be his only novel, The Picture of Dorian Gray (1890). The opportunity to construct aesthetic details precisely, and combine them with larger social themes, drew Wilde to write drama. He wrote Salome (1891) in French while in Paris but it was refused a licence for England due to an absolute prohibition on the portrayal of Biblical subjects on the English stage. Unperturbed, Wilde produced four society comedies in the early 1890s, which made him one of the most successful playwrights of late-Victorian London.
At the height of his fame and success, while The Importance of Being Earnest (1895) was still being performed in London, Wilde had the Marquess of Queensberry prosecuted for criminal libel. The Marquess was the father of Wilde's lover, Lord Alfred Douglas. The libel trial unearthed evidence that caused Wilde to drop his charges and led to his own arrest and trial for gross indecency with men. After two more trials he was convicted and sentenced to two years' hard labour, the maximum penalty, and was jailed from 1895 to 1897. During his last year in prison, he wrote De Profundis (published posthumously in 1905), a long letter which discusses his spiritual journey through his trials, forming a dark counterpoint to his earlier philosophy of pleasure. On his release, he left immediately for France, never to return to Ireland or Britain. There he wrote his last work, The Ballad of Reading Gaol (1898), a long poem commemorating the harsh rhythms of prison life.
Ray Douglas Bradbury (August 22, 1920 – June 5, 2012) was an American author and screenwriter.
He worked in a variety of genres, including fantasy, science fiction, horror, and mystery fiction.
Predominantly known for writing the iconic dystopian novel Fahrenheit 451 (1953), and his science-fiction and horror-story collections, The Martian Chronicles (1950), The Illustrated Man (1951), and I Sing the Body Electric (1969), Bradbury was one of the most celebrated 20th- and 21st-century American writers. While most of his best known work is in fantasy fiction, he also wrote in other genres, such as the coming-of-age novel Dandelion Wine (1957) and the fictionalized memoir Green Shadows, White Whale (1992).
Recipient of numerous awards, including a 2007 Pulitzer Citation, Bradbury also wrote and consulted on screenplays and television scripts, including Moby Dick and It Came from Outer Space. Many of his works were adapted to comic book, television, and film formats.
Upon his death in 2012, The New York Times called Bradbury "the writer most responsible for bringing modern science fiction into the literary mainstream".
Charles Michael Palahniuk (born February 21, 1962) is an American novelist and freelance journalist, who describes his work as transgressional fiction. He is the author of the award-winning novel Fight Club, which also was made into a popular film of the same name.
Erich Maria Remarque (born Erich Paul Remark; 22 June 1898 – 25 September 1970) was a 20th-century German novelist.
His landmark novel All Quiet on the Western Front (1928), about the German military experience of World War I, was an international best-seller which created a new literary genre, and was subsequently made into the cinema film All Quiet on the Western Front (1930).
Charles Lamb was an English essayist and poet, best known for his Essays of Elia and for the children's book Tales from Shakespeare, which he produced along with his sister, Mary Lamb.
Christian Otto Josef Wolfgang Morgenstern was a German author and poet from Munich. Morgenstern married Margareta Gosebruch von Liechtenstern on 7 March 1910.
Флетчер Нибел (англ. Fletcher Knebel) — американский журналист и писатель.
James Harlan Boren was an American who is best known as a humorist and writer on bureaucratese, in which he poked fun at what he called "the vacuumental thinking and idiotoxicities of Washington". He was also a businessman, teacher, scholar, public servant, political operative, presidential candidate, and public speaker.
James Branch Cabell was an American author of fantasy fiction and belles-lettres. Cabell was well-regarded by his contemporaries, including H. L. Mencken, Edmund Wilson, and Sinclair Lewis. His works were considered escapist and fit well in the culture of the 1920s, when they were most popular.
Mark Rutherford, pseudonym of William Hale White — English novelist noted for his studies of Nonconformist experience.
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan, (née Miller; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976) was an English writer.
She is known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving around her fictional detectives Hercule Poirot and Miss Marple. Christie also wrote the world's longest-running play, a murder mystery, The Mousetrap, and, under the pen name Mary Westmacott, six romances.
Isaac Asimov (; c. January 2, 1920 – April 6, 1992) was an American writer and professor of biochemistry at Boston University.
He was known for his works of science fiction and popular science. Asimov was a prolific writer who wrote or edited more than 500 books and an estimated 90,000 letters and postcards. His books have been published in 9 of the 10 major categories of the Dewey Decimal Classification.Asimov wrote hard science fiction. Along with Robert A. Heinlein and Arthur C. Clarke, Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers during his lifetime. Asimov's most famous work is the "Foundation" series, the first three books of which won the one-time Hugo Award for "Best All-Time Series" in 1966. His other major series are the "Galactic Empire" series and the Robot series. The Galactic Empire novels are set in earlier history of the same fictional universe as the Foundation series. Later, with Foundation and Earth (1986), he linked this distant future to the Robot stories, creating a unified "future history" for his stories much like those pioneered by Robert A. Heinlein and previously produced by Cordwainer Smith and Poul Anderson. He also wrote hundreds of short stories, including the social science fiction novelette "Nightfall", which in 1964 was voted the best short science fiction story of all time by the Science Fiction Writers of America. Asimov wrote the Lucky Starr series of juvenile science-fiction novels using the pen name Paul French.Asimov also wrote mysteries and fantasy, as well as much nonfiction. Most of his popular science books explain concepts in a historical way, going as far back as possible to a time when the science in question was at its simplest stage. Examples include Guide to Science, the three-volume set Understanding Physics, and Asimov's Chronology of Science and Discovery. He wrote on numerous other scientific and non-scientific topics, such as chemistry, astronomy, mathematics, history, biblical exegesis, and literary criticism.
He was president of the American Humanist Association. The asteroid 5020 Asimov, a crater on the planet Mars, a Brooklyn elementary school, and four literary awards are named in his honor.
Dame Jean Iris Murdoch (15 July 1919 – 8 February 1999) was a British novelist and philosopher.
Murdoch is best known for her novels about good and evil, sexual relationships, morality, and the power of the unconscious. Her first published novel, Under the Net, was selected in 1998 as one of Modern Library's 100 best English-language novels of the 20th century. In 1987, she was made a Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire. Her books include The Bell (1958), A Severed Head (1961), The Red and the Green (1965), The Nice and the Good (1968), The Black Prince (1973), Henry and Cato (1976), The Sea, the Sea (1978, Booker Prize), The Philosopher's Pupil (1983), The Good Apprentice (1985), The Book and the Brotherhood (1987), The Message to the Planet (1989), and The Green Knight (1993). In 2008, The Times ranked Murdoch twelfth on a list of "The 50 greatest British writers since 1945".
Alan Alexander Milne (18 January 1882 – 31 January 1956) was an English author, best known for his books about the teddy bear Winnie-the-Pooh and for various poems.
Milne was a noted writer, primarily as a playwright, before the huge success of Pooh overshadowed all his previous work. Milne served in both World Wars, joining the British Army in World War I, and was a captain of the British Home Guard in World War II.
Irwin Allen Ginsberg (June 3, 1926 – April 5, 1997) was an American poet, philosopher and writer.
He is considered to be one of the leading figures of both the Beat Generation during the 1950s and the counterculture that soon followed. He vigorously opposed militarism, economic materialism, and sexual repression and was known as embodying various aspects of this counterculture, such as his views on drugs, hostility to bureaucracy and openness to Eastern religions. He was one of many influential American writers of his time who were associated with the Beat Generation, including Jack Kerouac and William S. Burroughs.
Ginsberg is best known for his poem "Howl", in which he denounced what he saw as the destructive forces of capitalism and conformity in the United States. In 1956, "Howl" was seized by San Francisco police and US Customs. In 1957, it attracted widespread publicity when it became the subject of an obscenity trial, as it described heterosexual and homosexual sex at a time when sodomy laws made homosexual acts a crime in every U.S. state. "Howl" reflected Ginsberg's own sexuality and his relationships with a number of men, including Peter Orlovsky, his lifelong partner. Judge Clayton W. Horn ruled that "Howl" was not obscene, adding, "Would there be any freedom of press or speech if one must reduce his vocabulary to vapid innocuous euphemisms?"Ginsberg was a practicing Buddhist who studied Eastern religious disciplines extensively. He lived modestly, buying his clothing in second-hand stores and residing in downscale apartments in New York's East Village. One of his most influential teachers was the Tibetan Buddhist Chögyam Trungpa, the founder of the Naropa Institute in Boulder, Colorado. At Trungpa's urging, Ginsberg and poet Anne Waldman started The Jack Kerouac School of Disembodied Poetics there in 1974.Ginsberg took part in decades of non-violent political protest against everything from the Vietnam War to the War on Drugs. His poem "September on Jessore Road", calling attention to the plight of Bangladeshi refugees, exemplifies what the literary critic Helen Vendler described as Ginsberg's tireless persistence in protesting against "imperial politics, and persecution of the powerless."His collection The Fall of America shared the annual U.S. National Book Award for Poetry in 1974. In 1979, he received the National Arts Club gold medal and was inducted into the American Academy and Institute of Arts and Letters. Ginsberg was a Pulitzer Prize finalist in 1995 for his book Cosmopolitan Greetings: Poems 1986–1992.
Alphonse Allais (20 October 1854 – 28 October 1905) was a French writer and humorist, who was born in Honfleur, Calvados, and who died in Paris.
Alfred Louis Charles de Musset-Pathay (French: [al.fʁɛd də my.sɛ]; 11 December 1810 – 2 May 1857) was a French dramatist, poet, and novelist. Along with his poetry, he is known for writing the autobiographical novel La Confession d'un enfant du siècle (The Confession of a Child of the Century).
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was a British poet.
He was the Poet Laureate of Great Britain and Ireland during much of Queen Victoria's reign and remains one of the most popular British poets. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his first pieces, "Timbuktu". He published his first solo collection of poems, Poems Chiefly Lyrical in 1830. "Claribel" and "Mariana", which remain some of Tennyson's most celebrated poems, were included in this volume. Although decried by some critics as overly sentimental, his verse soon proved popular and brought Tennyson to the attention of well-known writers of the day, including Samuel Taylor Coleridge. Tennyson's early poetry, with its medievalism and powerful visual imagery, was a major influence on the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood.
Tennyson also excelled at penning short lyrics, such as "Break, Break, Break", "The Charge of the Light Brigade", "Tears, Idle Tears", and "Crossing the Bar". Much of his verse was based on classical mythological themes, such as "Ulysses", although "In Memoriam A.H.H." was written to commemorate his friend Arthur Hallam, a fellow poet and student at Trinity College, Cambridge, after he died of a stroke at the age of 22. Tennyson also wrote some notable blank verse including Idylls of the King, "Ulysses", and "Tithonus". During his career, Tennyson attempted drama, but his plays enjoyed little success.
A number of phrases from Tennyson's work have become commonplaces of the English language, including "Nature, red in tooth and claw" (In Memoriam A.H.H.), "'Tis better to have loved and lost / Than never to have loved at all", "Theirs not to reason why, / Theirs but to do and die", "My strength is as the strength of ten, / Because my heart is pure", "To strive, to seek, to find, and not to yield", "Knowledge comes, but Wisdom lingers", and "The old order changeth, yielding place to new". He is the ninth most frequently quoted writer in The Oxford Dictionary of Quotations.
Anatole France (French: [anatɔl fʁɑ̃s]; born François-Anatole Thibault, [frɑ̃swa anatɔl tibo]; 16 April 1844 – 12 October 1924) was a French poet, journalist, and novelist with several best-sellers.
Ironic and skeptical, he was considered in his day the ideal French man of letters. He was a member of the Académie française, and won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Literature "in recognition of his brilliant literary achievements, characterized as they are by a nobility of style, a profound human sympathy, grace, and a true Gallic temperament".France is also widely believed to be the model for narrator Marcel's literary idol Bergotte in Marcel Proust's In Search of Lost Time.
Anton Pavlovich Chekhov (Russian: Антон Павлович Чехов, tr. Antón Pávlovič Čéhov, IPA: [ɐnˈton ˈpavɫəvʲɪtɕ ˈtɕɛxəf]; 29 January 1860 – 15 July 1904) was a Russian playwright and short-story writer, who is considered to be among the greatest writers of short fiction in history.
His career as a playwright produced four classics, and his best short stories are held in high esteem by writers and critics. Along with Henrik Ibsen and August Strindberg, Chekhov is often referred to as one of the three seminal figures in the birth of early modernism in the theatre. Chekhov practiced as a medical doctor throughout most of his literary career: "Medicine is my lawful wife", he once said, "and literature is my mistress."Chekhov renounced the theatre after the reception of The Seagull in 1896, but the play was revived to acclaim in 1898 by Konstantin Stanislavski's Moscow Art Theatre, which subsequently also produced Chekhov's Uncle Vanya and premiered his last two plays, Three Sisters and The Cherry Orchard. These four works present a challenge to the acting ensemble as well as to audiences, because in place of conventional action Chekhov offers a "theatre of mood" and a "submerged life in the text".Chekhov had at first written stories to earn money, but as his artistic ambition grew, he made formal innovations which have influenced the evolution of the modern short story. He made no apologies for the difficulties this posed to readers, insisting that the role of an artist was to ask questions, not to answer them.
Arthur Bloch (born on January 1, 1948) is an American writer, author of the Murphy's Law books.
He has also written a self-help satire called Healing Yourself with Wishful Thinking. Since 1986 he has been the producer and director of the Thinking Allowed PBS television series.
The proper title of the book is Murphy's Law, and Other Reasons Why Things Go Wrong!. The word wrong is printed upside-down on the book's cover. This was the first of many Murphy's Law books.
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer, who created the character Sherlock Holmes.
Originally a physician, in 1887 he published A Study in Scarlet, the first of four novels and more than fifty short stories about Holmes and Dr. Watson. The Sherlock Holmes stories are generally considered milestones in the field of crime fiction.
Doyle was a prolific writer; other than Holmes stories, his works include fantasy and science fiction stories about Professor Challenger and humorous stories about the Napoleonic soldier Brigadier Gerard, as well as plays, romances, poetry, non-fiction and historical novels. One of Doyle's early short stories, "J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement", helped to popularise the mystery of the Mary Celeste.
Eugen Berthold Friedrich Brecht (10 February 1898 – 14 August 1956), known professionally as Bertolt Brecht, was a German theatre practitioner, playwright, and poet.
Coming of age during the Weimar Republic, he had his first successes as a playwright in Munich and moved to Berlin in 1924, where he wrote The Threepenny Opera with Kurt Weill and began a life-long collaboration with the composer Hanns Eisler. Immersed in Marxist thought during this period, he wrote didactic Lehrstücke and became a leading theoretician of epic theatre (which he later preferred to call "dialectical theatre") and the Verfremdungseffekt.
During the Nazi Germany period, Brecht fled his home country, first to Scandinavia, and during World War II to the United States, where he was surveilled by the FBI. After the war he was subpoenaed by the House Un-American Activities Committee. Returning to East Berlin after the war, he established the theatre company Berliner Ensemble with his wife and long-time collaborator, actress Helene Weigel.
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832) was a Scottish historical novelist, poet, playwright and historian.
Many of his works remain classics of both English-language literature and of Scottish literature. Famous titles include Ivanhoe, Rob Roy, Old Mortality, The Lady of the Lake, Waverley, The Heart of Midlothian and The Bride of Lammermoor.
Although primarily remembered for his extensive literary works and his political engagement, Scott was an advocate, judge and legal administrator by profession, and throughout his career combined his writing and editing work with his daily occupation as Clerk of Session and Sheriff-Depute of Selkirkshire.
A prominent member of the Tory establishment in Edinburgh, Scott was an active member of the Highland Society, served a long term as President of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1820–32) and was a Vice President of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland (1827-1829).Scott's knowledge of history, and his facility with literary technique, made him a seminal figure in the establishment of the historical novel genre, as well as an exemplar of European literary Romanticism.
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century.
He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and "The Legend of Sleepy Hollow" (1820), both of which appear in his collection The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent. His historical works include biographies of Oliver Goldsmith, Islamic prophet Muhammad, and George Washington, as well as several histories of 15th century Spain that deal with subjects such as Alhambra, Christopher Columbus, and the Moors.
Irving served as ambassador to Spain from 1842 to 1846. He made his literary debut in 1802 with a series of observational letters to the Morning Chronicle, written under the pseudonym Jonathan Oldstyle. He moved to England for the family business in 1815 where he achieved fame with the publication of The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent., serialized from 1819–20. He continued to publish regularly throughout his life, and he completed a five-volume biography of George Washington just eight months before his death at age 76 in Tarrytown, New York.
Irving was one of the first American writers to earn acclaim in Europe, and he encouraged other American authors such as Nathaniel Hawthorne, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe. He was also admired by some British writers, including Lord Byron, Thomas Campbell, Charles Dickens, Francis Jeffrey, and Walter Scott. He advocated for writing as a legitimate profession and argued for stronger laws to protect American writers from copyright infringement.
Publius Vergilius Maro (Classical Latin: [ˈpuː.blɪ.ʊs wɛrˈɡɪ.lɪ.ʊs ˈma.roː]; traditional dates October 15, 70 BC – September 21, 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil () in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period.
He wrote three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the Eclogues (or Bucolics), the Georgics, and the epic Aeneid. A number of minor poems, collected in the Appendix Vergiliana, are sometimes attributed to him.Virgil is traditionally ranked as one of Rome's greatest poets. His Aeneid has been considered the national epic of ancient Rome since the time of its composition. Modeled after Homer's Iliad and Odyssey, the Aeneid follows the Trojan refugee Aeneas as he struggles to fulfill his destiny and reach Italy, where his descendants Romulus and Remus were to found the city of Rome. Virgil's work has had wide and deep influence on Western literature, most notably Dante's Divine Comedy, in which Virgil appears as Dante's guide through Hell and Purgatory.
Adeline Virginia Woolf (née Stephen; 25 January 1882 – 28 March 1941) was an English writer, considered one of the most important modernist 20th-century authors and also a pioneer in the use of stream of consciousness as a narrative device.
Woolf was born into an affluent household in South Kensington, London, the seventh child in a blended family of eight. Her mother, Julia Prinsep Jackson, celebrated as a Pre-Raphaelite artist's model, had three children from her first marriage, while Woolf's father, Leslie Stephen, a notable man of letters, had one previous daughter. The Stephens produced another four children, including the modernist painter Vanessa Bell. While the boys in the family received college educations, the girls were home-schooled in English classics and Victorian literature. An important influence in Virginia Woolf's early life was the summer home the family used in St Ives, Cornwall, where she first saw the Godrevy Lighthouse, which was to become central in her novel To the Lighthouse (1927).
Woolf's childhood came to an abrupt end in 1895 with the death of her mother and her first mental breakdown, followed two years later by the death of her stepsister and a mother figure to her, Stella Duckworth. From 1897 to 1901, she attended the Ladies' Department of King's College London, where she studied classics and history and came into contact with early reformers of women's higher education and the women's rights movement. Other important influences were her Cambridge-educated brothers and unfettered access to her father's vast library.
Encouraged by her father, Woolf began writing professionally in 1900. Her father's death in 1905 caused another mental breakdown for Woolf. Following his death, the Stephen family moved from Kensington to the more bohemian Bloomsbury, where they adopted a free-spirited lifestyle. It was in Bloomsbury where, in conjunction with the brothers' intellectual friends, they formed the artistic and literary Bloomsbury Group.
Following her 1912 marriage to Leonard Woolf, the couple founded the Hogarth Press in 1917, which published much of her work. The couple rented a home in Sussex and moved there permanently in 1940. Throughout her life, Woolf was troubled by her mental illness. She was institutionalized several times and attempted suicide at least twice. Her illness is considered to have been bipolar disorder, for which there was no effective intervention during her lifetime. At age 59, Woolf committed suicide in 1941 by putting rocks in her coat pockets and drowning herself in the River Ouse.
During the interwar period, Woolf was an important part of London's literary and artistic society. In 1915 she published her first novel, The Voyage Out, through her half-brother's publishing house, Gerald Duckworth and Company. Her best-known works include the novels Mrs Dalloway (1925), To the Lighthouse (1927) and Orlando (1928). She is also known for her essays, including A Room of One's Own (1929), in which she wrote the much-quoted dictum, "A woman must have money and a room of her own if she is to write fiction."
Woolf became one of the central subjects of the 1970s movement of feminist criticism and her works have since garnered much attention and widespread commentary for "inspiring feminism." Her works have been translated into more than 50 languages. A large body of literature is dedicated to her life and work, and she has been the subject of plays, novels and films. Woolf is commemorated today by statues, societies dedicated to her work and a building at the University of London.
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817 – May 6, 1862) was an American essayist, poet, and philosopher.
A leading transcendentalist, Thoreau is best known for his book Walden, a reflection upon simple living in natural surroundings, and his essay "Civil Disobedience" (originally published as "Resistance to Civil Government"), an argument for disobedience to an unjust state.
Thoreau's books, articles, essays, journals, and poetry amount to more than 20 volumes. Among his lasting contributions are his writings on natural history and philosophy, in which he anticipated the methods and findings of ecology and environmental history, two sources of modern-day environmentalism. His literary style interweaves close observation of nature, personal experience, pointed rhetoric, symbolic meanings, and historical lore, while displaying a poetic sensibility, philosophical austerity, and Yankee attention to practical detail. He was also deeply interested in the idea of survival in the face of hostile elements, historical change, and natural decay; at the same time he advocated abandoning waste and illusion in order to discover life's true essential needs.He was a lifelong abolitionist, delivering lectures that attacked the Fugitive Slave Law while praising the writings of Wendell Phillips and defending the abolitionist John Brown. Thoreau's philosophy of civil disobedience later influenced the political thoughts and actions of such notable figures as Leo Tolstoy, Mahatma Gandhi, and Martin Luther King Jr.Thoreau is sometimes referred to as an anarchist. Though "Civil Disobedience" seems to call for improving rather than abolishing government—"I ask for, not at once no government, but at once a better government"—the direction of this improvement contrarily points toward anarchism: "'That government is best which governs not at all;' and when men are prepared for it, that will be the kind of government which they will have."
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator whose works include "Paul Revere's Ride", The Song of Hiawatha, and Evangeline.
He was also the first American to translate Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy and was one of the Fireside Poets from New England.
Longfellow was born in Portland, Maine, which was then still part of Massachusetts. He studied at Bowdoin College and, after spending time in Europe, he became a professor at Bowdoin and later at Harvard College. His first major poetry collections were Voices of the Night (1839) and Ballads and Other Poems (1841). Longfellow retired from teaching in 1854 to focus on his writing, and he lived the remainder of his life in a former Revolutionary War headquarters of George Washington in Cambridge, Massachusetts. His first wife Mary Potter died in 1835 after a miscarriage. His second wife Frances Appleton died in 1861 after sustaining burns when her dress caught fire. After her death, Longfellow had difficulty writing poetry for a time and focused on translating works from foreign languages. He died in 1882.
Longfellow wrote many lyric poems known for their musicality and often presenting stories of mythology and legend. He became the most popular American poet of his day and also had success overseas. He has been criticized, however, for imitating European styles and writing specifically for the masses.
Sir Henry Wotton (30 March 1568 – December 1639) was an English author, diplomat and politician who sat in the House of Commons in 1614 and 1625.
He is often quoted as saying, "An ambassador is an honest gentleman sent to lie abroad for the good of his country." (Wotton said that when on a mission in Augsburg, in 1604.)
Henry Fielding (22 April 1707 – 8 October 1754) was an English novelist and dramatist known for his rich, earthy humour and satirical prowess, and as the author of the picaresque novel Tom Jones.
Additionally, he holds a significant place in the history of law enforcement, having used his authority as a magistrate to found (with his half-brother John) what some have called London's first police force, the Bow Street Runners. His younger sister, Sarah, also became a successful writer.
Herbert George Wells (21 September 1866 – 13 August 1946) was an English writer.
He was prolific in many genres, writing dozens of novels, short stories, and works of social commentary, history, satire, biography, and autobiography, and even including two books on recreational war games. He is now best remembered for his science fiction novels and is often called the "father of science fiction", along with Jules Verne and Hugo Gernsback.During his own lifetime, however, he was most prominent as a forward-looking, even prophetic social critic who devoted his literary talents to the development of a progressive vision on a global scale. A futurist, he wrote a number of utopian works and foresaw the advent of aircraft, tanks, space travel, nuclear weapons, satellite television and something resembling the World Wide Web. His science fiction imagined time travel, alien invasion, invisibility, and biological engineering. Brian Aldiss referred to Wells as the "Shakespeare of science fiction". Wells rendered his works convincing by instilling commonplace detail alongside a single extraordinary assumption – dubbed “Wells’s law” – leading Joseph Conrad to hail him in 1898 as "O Realist of the Fantastic!". His most notable science fiction works include The Time Machine (1895), The Island of Doctor Moreau (1896), The Invisible Man (1897), The War of the Worlds (1898) and the military science fiction The War in the Air (1907). Wells was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature four times.Wells's earliest specialised training was in biology, and his thinking on ethical matters took place in a specifically and fundamentally Darwinian context. He was also from an early date an outspoken socialist, often (but not always, as at the beginning of the First World War) sympathising with pacifist views. His later works became increasingly political and didactic, and he wrote little science fiction, while he sometimes indicated on official documents that his profession was that of journalist. Novels such as Kipps and The History of Mr Polly, which describe lower-middle-class life, led to the suggestion that he was a worthy successor to Charles Dickens, but Wells described a range of social strata and even attempted, in Tono-Bungay (1909), a diagnosis of English society as a whole. Wells was a diabetic and co-founded the charity The Diabetic Association (known today as Diabetes UK) in 1934.
Guillaume Apollinaire (French: [ɡijom apɔlinɛʁ]; 26 August 1880 – 9 November 1918) was a French poet, playwright, short story writer, novelist, and art critic of Polish-Belarusian descent.
Apollinaire is considered one of the foremost poets of the early 20th century, as well as one of the most impassioned defenders of Cubism and a forefather of Surrealism. He is credited with coining the term "cubism" in 1911 to describe the emerging art movement and the term "surrealism" in 1917 to describe the works of Erik Satie. The term Orphism (1912) is also his. Apollinaire wrote one of the earliest Surrealist literary works, the play The Breasts of Tiresias (1917), which became the basis for Francis Poulenc's 1947 opera Les mamelles de Tirésias.
Apollinaire was active as a journalist and art critic for Le Matin, L'Intransigeant, L'Esprit nouveau, Mercure de France, and Paris Journal. In 1912 Apollinaire cofounded Les Soirées de Paris, an artistic and literary magazine.
Two years after being wounded in World War I, Apollinaire died in the Spanish flu pandemic of 1918; he was 38.
Howard Phillips Lovecraft (US: ; August 20, 1890 – March 15, 1937) was an American writer of weird fiction and horror fiction, who is known for his creation of what became the Cthulhu Mythos.Born in Providence, Rhode Island, Lovecraft spent most of his life in New England.
He was born into affluence, but the family's wealth dissipated soon after the death of his grandfather. In 1913, he wrote a critical letter to a pulp magazine that ultimately led to his involvement in pulp fiction. During the interwar period, he wrote and published stories that focused on his interpretation of humanity's place in the universe. In his view, humanity was an unimportant part of an uncaring cosmos that could be swept away at any moment. These stories also included fantastic elements that represented the perceived fragility of anthropocentrism.
Lovecraft was at the center of a wider body of authors known as "The Lovecraft Circle". This group wrote stories that frequently shared details among them. He was also a prolific writer of letters. He maintained a correspondence with several different authors and literary proteges. According to some estimates, he wrote approximately 100,000 letters over the course of his life. In these letters, he discussed his worldview and his daily life, and tutored younger authors, such as August Derleth, Donald Wandrei, and Robert Bloch.
Throughout his adult life, Lovecraft was never able to support himself from earnings as an author and editor. He was virtually unknown during his lifetime and was almost exclusively published in pulp magazines before he died in poverty at the age of 46, but is now regarded as one of the most significant 20th-century authors of supernatural horror fiction. Among his most celebrated tales are "The Call of Cthulhu", "The Rats in the Walls", At the Mountains of Madness, The Shadow over Innsmouth, and The Shadow Out of Time. His writings are the basis of the Cthulhu Mythos, which has inspired a large body of pastiches, games, music and other media drawing on Lovecraft's characters, setting and themes, constituting a wider subgenre known as Lovecraftian horror.
Eugene Luther Gore Vidal (born Eugene Louis Vidal, October 3, 1925 – July 31, 2012) was an American writer and public intellectual known for his patrician manner, epigrammatic wit, and polished style of writing.Vidal was born into a political family; his maternal grandfather, Thomas Pryor Gore, served as United States senator from Oklahoma (1907–1921 and 1931–1937). Vidal himself was a Democratic Party politician who twice sought elected office; first to the United States House of Representatives (New York, 1960), then to the U.S. Senate (California, 1982).As a political commentator and essayist, Vidal's principal subject was the history of the United States and its society, especially how the militaristic foreign policy reduced the country to a decadent empire.
His political and cultural essays were published in The Nation, the New Statesman, the New York Review of Books, and Esquire magazines. As a public intellectual, Gore Vidal's topical debates on sex, politics, and religion with other intellectuals and writers occasionally turned into quarrels with the likes of William F. Buckley Jr. and Norman Mailer. Vidal thought all men and women are potentially bisexual.As a novelist, Vidal explored the nature of corruption in public and private life. His polished and erudite style of narration readily evoked the time and place of his stories, and perceptively delineated the psychology of his characters. His third novel, The City and the Pillar (1948), offended the literary, political, and moral sensibilities of conservative book reviewers, the plot being about a dispassionately presented male homosexual relationship. In the historical novel genre, Vidal re-created the imperial world of Julian the Apostate (r. AD 361–63) in Julian (1964). Julian was the Roman emperor who used general religious toleration to re-establish pagan polytheism to counter the political subversion of Christian monotheism. In social satire, Myra Breckinridge (1968) explores the mutability of gender role and sexual orientation as being social constructs established by social mores. In Burr (1973) and Lincoln (1984), the protagonist is presented as "A Man of the People" and as "A Man" in a narrative exploration of how the public and private facets of personality affect the national politics of the United States.
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (8 December 65 BC – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his Odes as just about the only Latin lyrics worth reading: "He can be lofty sometimes, yet he is also full of charm and grace, versatile in his figures, and felicitously daring in his choice of words."Horace also crafted elegant hexameter verses (Satires and Epistles) and caustic iambic poetry (Epodes). The hexameters are amusing yet serious works, friendly in tone, leading the ancient satirist Persius to comment: "as his friend laughs, Horace slyly puts his finger on his every fault; once let in, he plays about the heartstrings".His career coincided with Rome's momentous change from a republic to an empire.
An officer in the republican army defeated at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BC, he was befriended by Octavian's right-hand man in civil affairs, Maecenas, and became a spokesman for the new regime. For some commentators, his association with the regime was a delicate balance in which he maintained a strong measure of independence (he was "a master of the graceful sidestep") but for others he was, in John Dryden's phrase, "a well-mannered court slave".
Decimus Iunius Iuvenalis (Latin: [ˈdɛ.kɪ.mʊs ˈjuː.ni.ʊs jʊ.wɛ.ˈnaː.lɪs]), known in English as Juvenal (), was a Roman poet active in the late first and early second century AD. He is the author of the collection of satirical poems known as the Satires.
The details of the author's life are unclear, although references within his text to known persons of the late first and early second centuries AD fix his earliest date of composition. One recent scholar argues that his first book was published in 100 or 101. Because of a reference to a recent political figure, his fifth and final surviving book must date from after 127.
Juvenal wrote at least 16 poems in the verse form dactylic hexameter. These poems cover a range of Roman topics. This follows Lucilius—the originator of the Roman satire genre, and it fits within a poetic tradition that also includes Horace and Persius. The Satires are a vital source for the study of ancient Rome from a number of perspectives, although their comic mode of expression makes it problematic to accept the content as strictly factual. At first glance the Satires could be read as a critique of pagan Rome. That critique may have ensured their survival in the Christian monastic scriptoria although the majority of ancient texts did not survive.
Jalāl ad-Dīn Muhammad Rūmī (Persian: جلالالدین محمد رومی), also known as Jalāl ad-Dīn Muhammad Balkhī (جلالالدین محمد بلخى), Mevlânâ/Mawlānā (مولانا, "our master"), Mevlevî/Mawlawī (مولوی, "my master"), and more popularly simply as Rumi (30 September 1207 – 17 December 1273), was a 13th-century Persian poet, faqih, Islamic scholar, theologian, and Sufi mystic originally from Greater Khorasan.
Rumi's influence transcends national borders and ethnic divisions: Iranians, Tajiks, Turks, Greeks, Pashtuns, other Central Asian Muslims, and the Muslims of South Asia have greatly appreciated his spiritual legacy for the past seven centuries. His poems have been widely translated into many of the world's languages and transposed into various formats. Rumi has been described as the "most popular poet" and the "best selling poet" in the United States.Rumi's works are written mostly in Persian, but occasionally he also used Turkish, Arabic, and Greek in his verse. His Masnavi (Mathnawi), composed in Konya, is considered one of the greatest poems of the Persian language. His works are widely read today in their original language across Greater Iran and the Persian-speaking world. Translations of his works are very popular, most notably in Turkey, Azerbaijan, the United States, and South Asia. His poetry has influenced not only Persian literature, but also the literary traditions of the Ottoman Turkish, Chagatai, Urdu and Pashto languages.
James Russell Lowell (February 22, 1819 – August 12, 1891) was an American Romantic poet, critic, editor, and diplomat.
He is associated with the Fireside Poets, a group of New England writers who were among the first American poets that rivaled the popularity of British poets. These writers usually used conventional forms and meters in their poetry, making them suitable for families entertaining at their fireside.
Lowell graduated from Harvard College in 1838, despite his reputation as a troublemaker, and went on to earn a law degree from Harvard Law School. He published his first collection of poetry in 1841 and married Maria White in 1844. The couple had several children, though only one survived past childhood. They soon became involved in the movement to abolish slavery, with Lowell using poetry to express his anti-slavery views and taking a job in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, as the editor of an abolitionist newspaper. After moving back to Cambridge, Lowell was one of the founders of a journal called The Pioneer, which lasted only three issues. He gained notoriety in 1848 with the publication of A Fable for Critics, a book-length poem satirizing contemporary critics and poets. The same year, he published The Biglow Papers, which increased his fame. He went on to publish several other poetry collections and essay collections throughout his literary career.
Maria died in 1853, and Lowell accepted a professorship of languages at Harvard in 1854; he continued to teach there for twenty years. He traveled to Europe before officially assuming his teaching duties in 1856, and married Frances Dunlap shortly thereafter in 1857. That year, Lowell also became editor of The Atlantic Monthly. It was not until 20 years later that he received his first political appointment, the ambassadorship to the Kingdom of Spain. He was later appointed ambassador to the Court of St. James's. He spent his last years in Cambridge in the same estate where he was born, and died there in 1891.
Lowell believed that the poet played an important role as a prophet and critic of society. He used poetry for reform, particularly in abolitionism. However, his commitment to the anti-slavery cause wavered over the years, as did his opinion on African-Americans. He attempted to emulate the true Yankee accent in the dialogue of his characters, particularly in The Biglow Papers. This depiction of the dialect, as well as his many satires, was an inspiration to writers such as Mark Twain and H. L. Mencken.
James Grover Thurber (December 8, 1894 – November 2, 1961) was an American cartoonist, author, humorist, journalist, playwright, and celebrated wit.
He was best known for his cartoons and short stories published mainly in The New Yorker magazine, such as "The Catbird Seat", and collected in his numerous books. He was one of the most popular humorists of his time, as he celebrated the comic frustrations and eccentricities of ordinary people. He wrote the Broadway comedy The Male Animal in collaboration with his college friend Elliott Nugent; it was later adapted into a film starring Henry Fonda and Olivia de Havilland. His short story "The Secret Life of Walter Mitty" has been adapted for film twice, once in 1947 and again in 2013.
Jack Kerouac (born Jean-Louis Kérouac (though he called himself Jean-Louis Lebris de Kérouac); March 12, 1922 – October 21, 1969) was an American novelist and poet of French-Canadian descent.He is considered a literary iconoclast and, alongside William S. Burroughs and Allen Ginsberg, a pioneer of the Beat Generation.
Kerouac is recognized for his method of spontaneous prose. Thematically, his work covers topics such as Catholic spirituality, jazz, promiscuity, Buddhism, drugs, poverty, and travel. He became an underground celebrity and, with other beats, a progenitor of the hippie movement, although he remained antagonistic toward some of its politically radical elements.In 1969, at age 47, Kerouac died from an abdominal hemorrhage caused by a lifetime of heavy drinking. Since his death, Kerouac's literary prestige has grown, and several previously unseen works have been published. All of his books are in print today, including The Town and the City, On the Road, Doctor Sax, The Dharma Bums, Mexico City Blues, The Subterraneans, Desolation Angels, Visions of Cody, The Sea Is My Brother, and Big Sur.
John Griffith London (born John Griffith Chaney; January 12, 1876 – November 22, 1916) was an American novelist, journalist, and social activist.
A pioneer in the world of commercial magazine fiction, he was one of the first writers to become a worldwide celebrity and earn a large fortune from writing. He was also an innovator in the genre that would later become known as science fiction.His most famous works include The Call of the Wild and White Fang, both set in the Klondike Gold Rush, as well as the short stories "To Build a Fire", "An Odyssey of the North", and "Love of Life". He also wrote about the South Pacific in stories such as "The Pearls of Parlay" and "The Heathen".
London was part of the radical literary group "The Crowd" in San Francisco and a passionate advocate of unionization, socialism, and the rights of workers. He wrote several powerful works dealing with these topics, such as his dystopian novel The Iron Heel, his non-fiction exposé The People of the Abyss, and The War of the Classes.
Jerome David Salinger (January 1, 1919 – January 27, 2010) was an American writer known for his novel The Catcher in the Rye.
He was raised in Manhattan and began writing short stories while in secondary school. His father urged him to learn about the meat-importing business; he went to work in Europe but was so disgusted by the slaughterhouses that he decided to embark on a different career path. He left Austria one month before it was annexed by Nazi Germany on March 12, 1938. In 1942, he began to date Oona O'Neill, daughter of playwright Eugene O'Neill. He found her self-absorbed, yet he called her often and wrote her long letters. Their relationship ended when Oona began seeing Charlie Chaplin, whom she eventually married.
In 1948, his story "A Perfect Day for Bananafish" appeared in The New Yorker magazine, which also published much of his later work. The Catcher in the Rye was published in novel form in 1951, having been serialised earlier. Many adolescent readers appreciated his depiction of adolescent alienation and loss of innocence in protagonist Holden Caulfield. The novel remains widely read and controversial, selling around 250,000 copies a year. The success of The Catcher in the Rye led to public attention and scrutiny, and Salinger became reclusive and led an obsessively private life for more than a half-century. He published his final work in 1965, and gave his last interview in 1980. He died of natural causes on January 27, 2010, at his home in Cornish, New Hampshire.
Jerome Klapka Jerome (2 May 1859 – 14 June 1927) was an English writer and humorist, best known for the comic travelogue Three Men in a Boat (1889).
Other works include the essay collections Idle Thoughts of an Idle Fellow (1886) and Second Thoughts of an Idle Fellow; Three Men on the Bummel, a sequel to Three Men in a Boat, and several other novels.
Geoffrey Chaucer (c. 1343 – 25 October 1400) was an English poet and author.
Widely considered the greatest English poet of the Middle Ages, he is best known for The Canterbury Tales. Chaucer has been styled the "Father of English literature" and was the first writer buried in Poets' Corner of Westminster Abbey.Chaucer also achieved fame in his lifetime as a philosopher and astronomer, composing the scientific A Treatise on the Astrolabe for his 10-year-old son Lewis. He maintained an active career in the civil service as a bureaucrat, courtier and diplomat. Among Chaucer's many other works are The Book of the Duchess, The House of Fame, The Legend of Good Women, and Troilus and Criseyde. He is seen as crucial in legitimising the literary use of the Middle English vernacular at a time when the dominant literary languages in England were still French and Latin.
Joanne Rowling ( "rolling"; born 31 July 1965), better known by her pen name J. K. Rowling, is a British author, film producer, television producer, screenwriter, and philanthropist.
She is best known for writing the Harry Potter fantasy series, which has won multiple awards and sold more than 500 million copies, becoming the best-selling book series in history. The books are the basis of a popular film series, over which Rowling had overall approval on the scripts and was a producer on the final films. She also writes crime fiction under the name Robert Galbraith.
Born in Yate, Gloucestershire, Rowling was working as a researcher and bilingual secretary for Amnesty International when she conceived the idea for the Harry Potter series while on a delayed train from Manchester to London in 1990. The seven-year period that followed saw the death of her mother, birth of her first child, divorce from her first husband, and relative poverty until the first novel in the series, Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone, was published in 1997. There were six sequels, of which the last, Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, was released in 2007. Since then, Rowling has written five books for adult readers: The Casual Vacancy (2012) and—under the pseudonym Robert Galbraith—the crime fiction Cormoran Strike series, which consists of The Cuckoo's Calling (2013), The Silkworm (2014), Career of Evil (2015), and Lethal White (2018).Rowling has lived a "rags to riches" life in which she progressed from living on benefits to being the world's first billionaire author. She lost her billionaire status after giving away much of her earnings to charity but remains one of the wealthiest people in the world. She is the UK's best-selling living author, with sales in excess of £238 million. The 2016 Sunday Times Rich List estimated Rowling's fortune at £600 million, ranking her as the joint 197th richest person in the UK. Time named her a runner-up for its 2007 Person of the Year, noting the social, moral, and political inspiration she has given her fans. In October 2010, Rowling was named the "Most Influential Woman in Britain" by leading magazine editors. She has supported multiple charities, including Comic Relief, One Parent Families, and Multiple Sclerosis Society of Great Britain, as well as launching her own charity, Lumos.
Joanne Michèle Sylvie Harris, (born 3 July 1964) is an English author especially known for her award-winning novel Chocolat (1999), which was adapted the following year for the film Chocolat.
Joseph Conrad (born Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski, Polish: [ˈjuzɛf tɛˈɔdɔr ˈkɔnrat kɔʐɛˈɲɔfskʲi] (listen); 3 December 1857 – 3 August 1924) was a Polish-British writer regarded as one of the greatest novelists to write in the English language.
Though he did not speak English fluently until his twenties, he was a master prose stylist who brought a non-English sensibility into English literature. Conrad wrote stories and novels, many with a nautical setting, that depict trials of the human spirit in the midst of what he saw as an impassive, inscrutable universe.Conrad is considered an early modernist, though his works contain elements of 19th-century realism. His narrative style and anti-heroic characters have influenced numerous authors, and many films have been adapted from, or inspired by, his works. Numerous writers and critics have commented that Conrad's fictional works, written largely in the first two decades of the 20th century, seem to have anticipated later world events.Writing near the peak of the British Empire, Conrad drew, among other things, on his native Poland's national experiences and on his own experiences in the French and British merchant navies, to create short stories and novels that reflect aspects of a European-dominated world—including imperialism and colonialism—and that profoundly explore the human psyche.
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( RUD-yərd; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936) was an English journalist, short-story writer, poet, and novelist. He was born in India, which inspired much of his work.
John Donne ( DUN; 22 January 1572 – 31 March 1631) was an English poet, scholar, soldier and secretary born into a recusant family, who later became a cleric in the Church of England.
Under royal patronage, he was made Dean of St Paul's Cathedral in London (1621–1631). He is considered the preeminent representative of the metaphysical poets. His poetical works are noted for their metaphorical and sensual style and include sonnets, love poems, religious poems, Latin translations, epigrams, elegies, songs, and satires. He is also known for his sermons.
Donne's style is characterised by abrupt openings and various paradoxes, ironies and dislocations. These features, along with his frequent dramatic or everyday speech rhythms, his tense syntax and his tough eloquence, were both a reaction against the smoothness of conventional Elizabethan poetry and an adaptation into English of European baroque and mannerist techniques. His early career was marked by poetry that bore immense knowledge of English society. Another important theme in Donne's poetry is the idea of true religion, something that he spent much time considering and about which he often theorised. He wrote secular poems as well as erotic and love poems. He is particularly famous for his mastery of metaphysical conceits.
Despite his great education and poetic talents, Donne lived in poverty for several years, relying heavily on wealthy friends. He spent much of the money he inherited during and after his education on womanising, literature, pastimes, and travel. In 1601, Donne secretly married Anne More, with whom he had twelve children. In 1615 he was ordained Anglican deacon and then priest, although he did not want to take holy orders and only did so because the king ordered it. He also served as a member of Parliament in 1601 and in 1614.
John Dryden (19 August [O.S. 9 August] 1631 – 12 May [O.S. 1 May] 1700) was an English poet, literary critic, translator, and playwright who was made England's first Poet Laureate in 1668.He is seen as dominating the literary life of Restoration England to such a point that the period came to be known in literary circles as the Age of Dryden.
Walter Scott called him "Glorious John".
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English Romantic poet.
He was one of the main figures of the second generation of Romantic poets, along with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley, despite his works having been in publication for only four years before his death from tuberculosis at the age of 25.Although his poems were not generally well received by critics during his lifetime, his reputation grew after his death, and by the end of the 19th century, he had become one of the most beloved of all English poets. He had a significant influence on a diverse range of poets and writers. Jorge Luis Borges stated that his first encounter with Keats' work was the most significant literary experience of his life.The poetry of Keats is characterised by sensual imagery, most notably in the series of odes. This is typical of romantic poets, as they aimed to accentuate extreme emotion through an emphasis on natural imagery. Today his poems and letters are some of the most popular and most analysed in English literature. Some of the most acclaimed works of Keats are "Ode to a Nightingale", "Sleep and Poetry", and the famous sonnet "On First Looking into Chapman's Homer".
John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet, polemicist, man of letters, and civil servant for the Commonwealth of England under its Council of State and later under Oliver Cromwell.
He wrote at a time of religious flux and political upheaval, and is best known for his epic poem Paradise Lost (1667), written in blank verse.
Writing in English, Latin, Greek, and Italian, he achieved international renown within his lifetime, and his celebrated Areopagitica (1644), written in condemnation of pre-publication censorship, is among history's most influential and impassioned defences of freedom of speech and freedom of the press. His desire for freedom extended into his style: he introduced new words (coined from Latin) to the English language, and was the first modern writer to employ non-rhymed verse outside of the theatre or translations.
William Hayley's 1796 biography called him the "greatest English author", and he remains generally regarded "as one of the preeminent writers in the English language", though critical reception has oscillated in the centuries since his death (often on account of his republicanism). Samuel Johnson praised Paradise Lost as "a poem which...with respect to design may claim the first place, and with respect to performance, the second, among the productions of the human mind", though he (a Tory and recipient of royal patronage) described Milton's politics as those of an "acrimonious and surly republican". Poets such as William Blake, William Wordsworth and Thomas Hardy revered him.
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien (3 January 1892 – 2 September 1973) was an English writer, poet, philologist, and academic, who is best known as the author of the classic high fantasy works The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion.
He served as the Rawlinson and Bosworth Professor of Anglo-Saxon and Fellow of Pembroke College, Oxford, from 1925 to 1945 and Merton Professor of English Language and Literature and Fellow of Merton College, Oxford, from 1945 to 1959. He was at one time a close friend of C. S. Lewis—they were both members of the informal literary discussion group known as the Inklings. Tolkien was appointed a Commander of the Order of the British Empire by Queen Elizabeth II on 28 March 1972.
After Tolkien's death, his son Christopher published a series of works based on his father's extensive notes and unpublished manuscripts, including The Silmarillion. These, together with The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, form a connected body of tales, poems, fictional histories, invented languages, and literary essays about a fantasy world called Arda and Middle-earth within it. Between 1951 and 1955, Tolkien applied the term legendarium to the larger part of these writings.While many other authors had published works of fantasy before Tolkien, the great success of The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings led directly to a popular resurgence of the genre. This has caused Tolkien to be popularly identified as the "father" of modern fantasy literature—or, more precisely, of high fantasy. In 2008, The Times ranked him sixth on a list of "The 50 greatest British writers since 1945". Forbes ranked him the fifth top-earning "dead celebrity" in 2009.
John Ernst Steinbeck Jr. (February 27, 1902 – December 20, 1968) was an American author.
He won the 1962 Nobel Prize in Literature "for his realistic and imaginative writings, combining as they do sympathetic humour and keen social perception." He has been called "a giant of American letters," and many of his works are considered classics of Western literature.During his writing career, he authored 27 books, including 16 novels, six non-fiction books, and two collections of short stories. He is widely known for the comic novels Tortilla Flat (1935) and Cannery Row (1945), the multi-generation epic East of Eden (1952), and the novellas Of Mice and Men (1937) and The Red Pony (1937). The Pulitzer Prize-winning The Grapes of Wrath (1939) is considered Steinbeck's masterpiece and part of the American literary canon. In the first 75 years after it was published, it sold 14 million copies.Most of Steinbeck's work is set in central California, particularly in the Salinas Valley and the California Coast Ranges region. His works frequently explored the themes of fate and injustice, especially as applied to downtrodden or everyman protagonists.
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish satirist, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whigs, then for the Tories), poet and cleric who became Dean of St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin.Swift is remembered for works such as A Tale of a Tub (1704), An Argument Against Abolishing Christianity (1712), Gulliver's Travels (1726), and A Modest Proposal (1729). He is regarded by the Encyclopædia Britannica as the foremost prose satirist in the English language, and is less well known for his poetry.
He originally published all of his works under pseudonyms – such as Lemuel Gulliver, Isaac Bickerstaff, M. B. Drapier – or anonymously. He was a master of two styles of satire, the Horatian and Juvenalian styles.
His deadpan, ironic writing style, particularly in A Modest Proposal, has led to such satire being subsequently termed "Swiftian".
George Herbert (3 April 1593 – 1 March 1633) was a Welsh-born poet, orator, and priest of the Church of England.
His poetry is associated with the writings of the metaphysical poets, and he is recognised as "one of the foremost British devotional lyricists." He was born into an artistic and wealthy family and largely raised in England. He received a good education that led to his admission to Trinity College, Cambridge in 1609. He went there with the intention of becoming a priest, but he became the University's Public Orator and attracted the attention of King James I. He served in the Parliament of England in 1624 and briefly in 1625.
Josh Billings was the pen name of 19th-century American humorist Henry Wheeler Shaw (April 21, 1818 – October 14, 1885). He was a famous humor writer and lecturer in the United States during the latter half of the 19th century. He is often compared to Mark Twain.
Dylan Marlais Thomas (27 October 1914 – 9 November 1953) was a Welsh poet and writer whose works include the poems "Do not go gentle into that good night" and "And death shall have no dominion"; the 'play for voices' Under Milk Wood; and stories and radio broadcasts such as A Child's Christmas in Wales and Portrait of the Artist as a Young Dog.
He became widely popular in his lifetime and remained so after his premature death at the age of 39 in New York City. By then he had acquired a reputation, which he had encouraged, as a "roistering, drunken and doomed poet".
Theodor Seuss Geisel (March 2, 1904 – September 24, 1991) was an American children's author, political cartoonist, illustrator, poet, animator, screenwriter, and filmmaker.
He is known for his work writing and illustrating more than 60 books under the pen name Doctor Seuss ( or abbreviated Dr. Seuss). His work includes many of the most popular children's books of all time, selling over 600 million copies and being translated into more than 20 languages by the time of his death.Geisel adopted the name "Dr. Seuss" as an undergraduate at Dartmouth College and as a graduate student at Lincoln College, Oxford. He left Oxford in 1927 to begin his career as an illustrator and cartoonist for Vanity Fair, Life, and various other publications. He also worked as an illustrator for advertising campaigns, most notably for FLIT and Standard Oil, and as a political cartoonist for the New York newspaper PM. He published his first children's book And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street in 1937. During World War II, he took a brief hiatus from children's literature to illustrate political cartoons, and he also worked in the animation and film department of the United States Army where he wrote, produced or animated many productions – both live-action and animated – including Design for Death, which later won the 1947 Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature.After the war, Geisel returned to writing children's books, writing classics like If I Ran the Zoo (1950), Horton Hears a Who! (1955), If I Ran the Circus (1956), The Cat in the Hat (1957), How the Grinch Stole Christmas! (1957), and Green Eggs and Ham (1960). He published over 60 books during his career, which have spawned numerous adaptations, including 11 television specials, five feature films, a Broadway musical, and four television series.
Geisel won the Lewis Carroll Shelf Award in 1958 for Horton Hatches the Egg and again in 1961 for And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street. Geisel's birthday, March 2, has been adopted as the annual date for National Read Across America Day, an initiative on reading created by the National Education Association.
Dorothy Parker (née Rothschild; August 22, 1893 – June 7, 1967) was an American poet, writer, critic, and satirist based in New York; she was best known for her wit, wisecracks, and eye for 20th-century urban foibles.
From a conflicted and unhappy childhood, Parker rose to acclaim, both for her literary works published in such magazines as The New Yorker and as a founding member of the Algonquin Round Table. Following the breakup of the circle, Parker traveled to Hollywood to pursue screenwriting. Her successes there, including two Academy Award nominations, were curtailed when her involvement in left-wing politics resulted in her being placed on the Hollywood blacklist.
Dismissive of her own talents, she deplored her reputation as a "wisecracker". Nevertheless, both her literary output and reputation for sharp wit have endured.
Douglas Noel Adams (11 March 1952 – 11 May 2001) was an English author, screenwriter, essayist, humorist, satirist and dramatist.
Adams was author of The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy, which originated in 1978 as a BBC radio comedy before developing into a "trilogy" of five books that sold more than 15 million copies in his lifetime and generated a television series, several stage plays, comics, a video game, and in 2005 a feature film. Adams's contribution to UK radio is commemorated in The Radio Academy's Hall of Fame.Adams also wrote Dirk Gently's Holistic Detective Agency (1987) and The Long Dark Tea-Time of the Soul (1988), and co-wrote The Meaning of Liff (1983), The Deeper Meaning of Liff (1990), Last Chance to See (1990), and three stories for the television series Doctor Who; he also served as script editor for the show's seventeenth season in 1979. He also co-wrote the Monty Python sketch “Patient Abuse” which appeared in the final episode of Monty Python's Flying Circus. A posthumous collection of his works, including an unfinished novel, was published as The Salmon of Doubt in 2002.
Adams was an advocate for environmentalism and conservation, a lover of fast cars, technological innovation and the Apple Macintosh, and a self-proclaimed radical atheist.
Jean de La Fontaine (UK: , US: , French: [ʒɑ̃ d(ə) la fɔ̃tɛn]; 8 July 1621 – 13 April 1695) was a French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century.
He is known above all for his Fables, which provided a model for subsequent fabulists across Europe and numerous alternative versions in France, and in French regional languages.
After a long period of royal suspicion, he was admitted to the French Academy and his reputation in France has never faded since. Evidence of this is found in the many pictures and statues of the writer, as well as later depictions on medals, coins and postage stamps.
Jean-Pierre Claris de Florian (March 6, 1755 in château of Florian, near Sauve, Gard – September 13, 1794 in Sceaux) was a French poet and romance writer.
Amantine Lucile Aurore Dupin de Francueil (French: [amɑ̃tin lysil oʁɔʁ dypɛ̃]; 1 July 1804 – 8 June 1876), best known by her pen name George Sand (French: [ʒɔʁʒ sɑ̃d]), was a French novelist, memoirist, and journalist.
One of the most popular writers in Europe in her lifetime, being more renowned than both Victor Hugo and Honoré de Balzac in England in the 1830s and 1840s, Sand is recognised as one of the most notable writers of the European Romantic era, with more than 70 novels to her credit and 50 volumes of various works including novels, tales, plays and political texts.
Like her great-grandmother, Louise Dupin, whom she admired, George Sand stood up for women, advocated passion, castigated marriage and fought against the prejudices of a conservative society.
Pierre-Jules Renard or Jules Renard (22 February 1864 – 22 May 1910) was a French author and member of the Académie Goncourt, most famous for the works Poil de carotte (Carrot Top, 1894) and Les Histoires Naturelles (Nature Stories, 1896). Among his other works are Le Plaisir de rompre (The Pleasure of Breaking, 1898) and the posthumously published Huit Jours à la campagne (A Week in the Country, 1912).
Julien Green (September 6, 1900 – August 13, 1998) was an American writer who authored several novels (The Dark Journey, The Closed Garden, Moira, Each Man in His Darkness, the Dixie trilogy, etc.), a four-volume autobiography (The Green Paradise, The War at Sixteen, Love in America and Restless Youth) and his famous Diary (in nineteen volumes, 1919–1998). He wrote primarily in French and was the first non-French national to be elected to the Académie française.
Jerome (Latin: Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; Greek: Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; c. 347 – 30 September 420) was a Latin Catholic priest, confessor, theologian, and historian, commonly known as Saint Jerome.
He was born at Stridon, a village near Emona on the border of Dalmatia and Pannonia. He is best known for his translation of most of the Bible into Latin (the translation that became known as the Vulgate), and his commentaries on the Gospels. His list of writings is extensive.The protégé of Pope Damasus I, who died in December of 384, Jerome was known for his teachings on Christian moral life, especially to those living in cosmopolitan centers such as Rome. In many cases, he focused his attention on the lives of women and identified how a woman devoted to Jesus should live her life. This focus stemmed from his close patron relationships with several prominent female ascetics who were members of affluent senatorial families.Jerome is recognised as a saint and Doctor of the Church by the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Lutheran Church, and the Anglican Communion. His feast day is 30 September.
Carlos Castaneda (December 25, 1925–April 27, 1998) was an American author.
Starting with The Teachings of Don Juan in 1968, Castaneda wrote a series of books that describe his training in shamanism, particularly with a group whose lineage descended from the Toltecs. The books, narrated in the first person, relate his experiences under the tutelage of a man that Castaneda claimed was a Yaqui "Man of Knowledge" named don Juan Matus. His 12 books have sold more than 28 million copies in 17 languages. Critics have suggested that they are works of fiction; supporters claim the books are either true or at least valuable works of philosophy.
Castaneda withdrew from public view in 1973, living in a large house in Westwood, California from 1973 until his death in 1998, with three colleagues whom he called "Fellow Travellers of Awareness." He founded Cleargreen, an organization that promotes "Tensegrity", which Castaneda described as the modern version of the "magical passes" of the shamans of ancient Mexico.
Claudius Claudianus, usually known in English as Claudian (c. 370 – c. 404 AD), was a Latin poet associated with the court of the emperor Honorius at Mediolanum (Milan), and particularly with the general Stilicho.
His work, written almost entirely in hexameters or elegiac couplets, falls into three main categories: poems for Honorius, poems for Stilicho, and mythological epic.
Clive Staples Lewis (29 November 1898 – 22 November 1963) was a British writer and lay theologian.
He held academic positions in English literature at both Oxford University (Magdalen College, 1925–1954) and Cambridge University (Magdalene College, 1954–1963). He is best known for his works of fiction, especially The Screwtape Letters, The Chronicles of Narnia, and The Space Trilogy, and for his non-fiction Christian apologetics, such as Mere Christianity, Miracles, and The Problem of Pain.
Kurt Vonnegut Jr. (November 11, 1922 – April 11, 2007) was an American writer.
In a career spanning over 50 years, Vonnegut published fourteen novels, three short story collections, five plays, and five works of non-fiction, with further collections being published after his death. He is most famous for his darkly satirical, best-selling novel Slaughterhouse-Five (1969).
Born and raised in Indianapolis, Indiana, Vonnegut attended Cornell University but dropped out in January 1943 and enlisted in the United States Army. As part of his training, he studied mechanical engineering at Carnegie Institute of Technology (now Carnegie Mellon University) and the University of Tennessee. He was then deployed to Europe to fight in World War II and was captured by the Germans during the Battle of the Bulge. He was interned in Dresden and survived the Allied bombing of the city by taking refuge in a meat locker of the slaughterhouse where he was imprisoned. After the war, Vonnegut married Jane Marie Cox, with whom he had three children. He later adopted his sister's three sons, after she died of cancer and her husband was killed in a train accident.
Vonnegut published his first novel, Player Piano, in 1952. The novel was reviewed positively but was not commercially successful. In the nearly 20 years that followed, Vonnegut published several novels that were only marginally successful, such as Cat's Cradle (1963) and God Bless You, Mr. Rosewater (1964). Vonnegut's breakthrough was his commercially and critically successful sixth novel, Slaughterhouse-Five. The book's anti-war sentiment resonated with its readers amidst the ongoing Vietnam War and its reviews were generally positive. After its release, Slaughterhouse-Five went to the top of The New York Times Best Seller list, thrusting Vonnegut into fame. He was invited to give speeches, lectures and commencement addresses around the country and received many awards and honors.
Later in his career, Vonnegut published several autobiographical essays and short-story collections, including Fates Worse Than Death (1991), and A Man Without a Country (2005). After his death, he was hailed as a morbidly comical commentator on the society in which he lived and as one of the most important contemporary writers. Vonnegut's son Mark published a compilation of his father's unpublished compositions, titled Armageddon in Retrospect. In 2017, Seven Stories Press published Complete Stories, a collection of Vonnegut's short fiction including five previously unpublished stories. Complete Stories was collected and introduced by Vonnegut friends and scholars Jerome Klinkowitz and Dan Wakefield. Numerous scholarly works have examined Vonnegut's writing and humor.
Kathleen Thompson Norris (July 16, 1880 – January 18, 1966) was an American novelist and newspaper columnist.
She was one of the most widely read and highest paid female writers in the United States for nearly fifty years, from 1911 to 1959. Norris was a prolific writer who wrote 93 novels, many of which became best sellers. Her stories appeared frequently in the popular press of the day, including Atlantic, The American Magazine, McClure's, Everybody's, Ladies' Home Journal and Woman's Home Companion. Norris used her fiction to promote family and moralistic values, such as the sanctity of marriage, the nobility of motherhood, and the importance of service to others.
Loretta "Letty" Cottin Pogrebin (born June 9, 1939) is an American author, journalist, lecturer, and social activist.
She is a founding editor of Ms. magazine, the author of eleven books, and was an editorial consultant for the TV special Free to Be... You and Me (as well as for the album and book associated with it) for which she earned an Emmy.
Lina Vasylivna Kostenko (Ukrainian: Ліна Василівна Костенко; born 19 March 1930) is a Ukrainian poet, journalist, writer, publisher, and former Soviet dissident.
A founder and leading representative of the Sixtiers poetry movement, Kostenko has been described as one of Ukraine's foremost poets and credited with reviving Ukrainian-language lyric poetry.
Kostenko has been granted numerous honours, including an honorary professorship at Kyiv Mohyla Academy, honorary doctorates of Lviv and Chernivtsi Universities, and the Shevchenko National Prize, Legion of Honour.
Laurence Sterne (24 November 1713 – 18 March 1768) was an Irish novelist and an Anglican clergyman.
He wrote the novels The Life and Opinions of Tristram Shandy, Gentleman and A Sentimental Journey Through France and Italy, and also published many sermons, wrote memoirs, and was involved in local politics. Sterne died in London after years of fighting tuberculosis.
Max Rudolf Frisch (15 May 1911 – 4 April 1991) was a Swiss playwright and novelist.
Frisch's works focused on problems of identity, individuality, responsibility, morality, and political commitment. The use of irony is a significant feature of his post-war output. Frisch was one of the founders of Gruppe Olten. He was awarded the Neustadt International Prize for Literature in 1986.
Margaret Eleanor Atwood (born November 18, 1939) is a Canadian poet, novelist, literary critic, essayist, inventor, teacher, and environmental activist.
Since 1961, she has published 17 books of poetry, 16 novels, 10 books of non-fiction, eight collections of short fiction, eight children's books, and one graphic novel, as well as a number of small press editions in poetry and fiction. Atwood has won numerous awards and honors for her writing, including the Man Booker Prize, Arthur C. Clarke Award, Governor General's Award, Franz Kafka Prize, and the National Book Critics and PEN Center USA Lifetime Achievement Awards.
Atwood is also the inventor and developer of the LongPen and associated technologies that facilitate remote robotic writing of documents. A number of her works have been adapted for film and television, increasing her exposure.
Atwood's works encompass a variety of themes including gender and identity, religion and myth, the power of language, climate change, and "power politics". Many of her poems are inspired by myths and fairy tales which interested her from a very early age. Atwood is a founder of the Griffin Poetry Prize and Writers' Trust of Canada. She is also a Senior Fellow of Massey College, Toronto.
Marge Piercy (born March 31, 1936) is an American progressive activist and writer.
Her work includes Woman on the Edge of Time; He, She and It, which won the 1993 Arthur C. Clarke Award; and Gone to Soldiers, a New York Times Best Seller and a sweeping historical novel set during World War II. Piercy's work is rooted in her Jewish heritage, Communist social and political activism, and feminist ideals.
Cato the Elder (Latin: Cato Major; 234–149 BC), born Marcus Porcius Cato and also known as Cato the Censor (Cato Censorius), Cato the Wise (Cato Sapiens), and Cato the Ancient (Cato Priscus), was a Roman soldier, senator and historian known for his conservatism and opposition to Hellenization.
He was the first to write history in Latin.
Milan Kundera is a Czech writer who went into exile in France in 1975, becoming a naturalised French citizen in 1981. Kundera's Czechoslovak citizenship was revoked in 1979, then conferred again in 2019.
Milorad Pavić (Serbian Cyrillic: Милорад Павић, pronounced [mîloraːd pǎːʋitɕ]; 15 October 1929 – 30 November 2009) was a Serbian novelist, poet, short story writer, and literary historian.
Born in Belgrade in 1929, he published a number of poems, short stories and novels during his lifetime, the most famous of which was the Dictionary of the Khazars (1984). Upon its release, it was hailed as "the first novel of the 21st century." Pavić's works have been translated into more than thirty languages. He was vastly popular in Europe and in South America, and was deemed "one of the most intriguing writers from the beginning of the 21st century." He won numerous prizes in Serbia and in the former Yugoslavia, and was mentioned several times as a potential candidate for the Nobel Prize in Literature. He died in Belgrade in 2009.
Maurice Polydore Marie Bernard Maeterlinck (29 August 1862 – 6 May 1949), also known as Count (or Comte) Maeterlinck from 1932, was a Belgian playwright, poet, and essayist who was Flemish but wrote in French.
He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1911 "in appreciation of his many-sided literary activities, and especially of his dramatic works, which are distinguished by a wealth of imagination and by a poetic fancy, which reveals, sometimes in the guise of a fairy tale, a deep inspiration, while in a mysterious way they appeal to the readers' own feelings and stimulate their imaginations". The main themes in his work are death and the meaning of life. He was a leading member of La Jeune Belgique group and his plays form an important part of the Symbolist movement.
May Sarton is the pen name of Eleanore Marie Sarton, a prolific American poet, novelist and memoirist.
She is considered an important contemporary figure in American literature, as well as a "poet's poet", and is lauded by literary and feminist critics for her works addressing themes in gender, sexuality, and universality.
Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman (born Neil Richard Gaiman, 10 November 1960) is an English author of short fiction, novels, comic books, graphic novels, nonfiction, audio theatre, and films.
His works include the comic book series The Sandman and novels Stardust, American Gods, Coraline, and The Graveyard Book. He has won numerous awards, including the Hugo, Nebula, and Bram Stoker awards, as well as the Newbery and Carnegie medals. He is the first author to win both the Newbery and the Carnegie medals for the same work, The Graveyard Book (2008). In 2013, The Ocean at the End of the Lane was voted Book of the Year in the British National Book Awards.
Norman Vincent Peale (May 31, 1898 – December 24, 1993) was an American minister and author known for his work in popularizing the concept of positive thinking, especially through his best-selling book The Power of Positive Thinking.
He served as the pastor of Marble Collegiate Church, New York, from 1932 until his death, leading a Reformed Church in America congregation. Peale was a personal friend of President Richard Nixon. Donald Trump attended Peale's church while growing up, as well as marrying his first wife Ivana there. Peale's ideas and techniques were controversial, and he received frequent criticism both from church figures and from the psychiatric profession.
Frederic Ogden Nash (August 19, 1902 – May 19, 1971) was an American poet well known for his light verse, of which he wrote over 500 pieces. With his unconventional rhyming schemes, he was declared the country's best-known producer of humorous poetry.
Octavio Paz Lozano (March 31, 1914 – April 19, 1998) was a Mexican poet and diplomat. For his body of work, he was awarded the 1981 Miguel de Cervantes Prize, the 1982 Neustadt International Prize for Literature, and the 1990 Nobel Prize in Literature.
Aldous Leonard Huxley (26 July 1894 – 22 November 1963) was an English writer and philosopher.
He authored nearly fifty books—both novels and non-fiction works—as well as wide-ranging essays, narratives, and poems.
Born into the prominent Huxley family, he graduated from Balliol College, Oxford with an undergraduate degree in English literature. Early in his career, he published short stories and poetry and edited the literary magazine Oxford Poetry, before going on to publish travel writing, satire, and screenplays. He spent the latter part of his life in the United States, living in Los Angeles from 1937 until his death. By the end of his life, Huxley was widely acknowledged as one of the foremost intellectuals of his time. He was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature seven times and was elected Companion of Literature by the Royal Society of Literature in 1962.Huxley was a humanist and pacifist. He grew interested in philosophical mysticism and universalism, addressing these subjects with works such as The Perennial Philosophy (1945)—which illustrates commonalities between Western and Eastern mysticism—and The Doors of Perception (1954)—which interprets his own psychedelic experience with mescaline. In his most famous novel Brave New World (1932) and his final novel Island (1962), he presented his vision of dystopia and utopia, respectively.
Honoré de Balzac was a French novelist and playwright.
Pliny the Elder (born Gaius Plinius Secundus, AD 23–79) was a Roman author, a naturalist and natural philosopher, a naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of emperor Vespasian.
Pliny wrote the encyclopedic Naturalis Historia (Natural History), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias.
He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field.
His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus:
For my part I deem those blessed to whom, by favour of the gods, it has been granted either to do what is worth writing of, or to write what is worth reading; above measure blessed those on whom both gifts have been conferred. In the latter number will be my uncle, by virtue of his own and of your compositions.
Pliny the Younger refers to Tacitus’s reliance upon his uncle's book, the History of the German Wars.
Pliny the Elder died in AD 79 in Stabiae while attempting the rescue of a friend and his family by ship from the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, which had already destroyed the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. The wind caused by the sixth and largest pyroclastic surge of the volcano’s eruption did not allow his ship to leave port, and Pliny probably died during that event.
Paul-Marie Verlaine (; French: [vɛʁlɛn(ə)]; 30 March 1844 – 8 January 1896) was a French poet associated with the Symbolist movement and the Decadent movement. He is considered one of the greatest representatives of the fin de siècle in international and French poetry.
Publius Ovidius Naso (Classical Latin: [ˈpu:.blɪ.ʊs ɔˈwɪ.dɪ.ʊs ˈnaː.soː]; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known as Ovid () in the English-speaking world, was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus.
He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the three canonical poets of Latin literature. The Imperial scholar Quintilian considered him the last of the Latin love elegists. He enjoyed enormous popularity, but, in one of the mysteries of literary history, was sent by Augustus into exile in a remote province on the Black Sea, where he remained until his death. Ovid himself attributes his exile to carmen et error, "a poem and a mistake", but his discretion in discussing the causes has resulted in much speculation among scholars.
The first major Roman poet to begin his career during the reign of Augustus, Ovid is today best known for the Metamorphoses, a 15-book continuous mythological narrative written in the meter of epic, and for works in elegiac couplets such as Ars Amatoria ("The Art of Love") and Fasti. His poetry was much imitated during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, and greatly influenced Western art and literature. The Metamorphoses remains one of the most important sources of classical mythology.
Pierre-Jean de Béranger (19 August 1780 – 16 July 1857) was a prolific French poet and chansonnier (songwriter), who enjoyed great popularity and influence in France during his lifetime, but faded into obscurity in the decades following his death.
He has been described as "the most popular French songwriter of all time" and "the first superstar of French popular music".
René Karl Wilhelm Johann Josef Maria Rilke (4 December 1875 – 29 December 1926), better known as Rainer Maria Rilke (German: [ˈʁaɪnɐ maˈʁiːa ˈʁɪlkə]), was an Austrian poet and novelist.
He is "widely recognized as one of the most lyrically intense German-language poets". He wrote both verse and highly lyrical prose. Several critics have described Rilke's work as "mystical". His writings include one novel, several collections of poetry and several volumes of correspondence in which he invokes images that focus on the difficulty of communion with the ineffable in an age of disbelief, solitude and anxiety. These themes position him as a transitional figure between traditional and modernist writers.
Rilke travelled extensively throughout Europe (including Russia, Spain, Germany, France and Italy) and, in his later years, settled in Switzerland – settings that were key to the genesis and inspiration for many of his poems. While Rilke is most known for his contributions to German literature, over 400 poems were originally written in French and dedicated to the canton of Valais in Switzerland. Among English-language readers, his best-known works include the poetry collections Duino Elegies (Duineser Elegien) and Sonnets to Orpheus (Die Sonette an Orpheus), the semi-autobiographical novel The Notebooks of Malte Laurids Brigge (Die Aufzeichnungen des Malte Laurids Brigge), and a collection of ten letters that was published after his death under the title Letters to a Young Poet (Briefe an einen jungen Dichter). In the later 20th century, his work found new audiences through use by New Age theologians and self-help authors and frequent quotations by television programs, books and motion pictures. In the United States, Rilke remains among the more popular, best-selling poets.
Rita Mae Brown (born November 28, 1944) is an American writer, activist, and feminist. She is best known for her first novel, Rubyfruit Jungle. Brown is also a mystery writer and screenwriter.
Richard David Bach (born June 23, 1936) is an American writer.
Bach is widely known as the author of some of the 1970s' biggest sellers, including Jonathan Livingston Seagull (1970) and Illusions: The Adventures of a Reluctant Messiah (1977). Bach has written numerous works of fiction, and also non-fiction flight-related titles.
Most of Bach's books have been semi-autobiographical, using actual or fictionalized events from his life to illustrate his philosophy. Bach's books espouse his philosophy that our apparent physical limits and mortality are merely appearance. Bach is noted for his love of aviation and for his books related to flying in a metaphorical context. Bach has pursued flying as a hobby since the age of 17. In late August 2012, Bach was badly injured when on approach to landing at Friday Harbor, Washington, his aircraft clipped some power lines and crashed upside down in a field.
Richard Gary Brautigan (January 30, 1935 – ca. September 16, 1984) was an American novelist, poet, and short story writer.
His work often employs black comedy, parody, and satire. He is best known for his novels Trout Fishing in America (1967) and In Watermelon Sugar (1968).
Brautigan began his career as a poet, with his first collection being published in 1957. He made his debut as a novelist with A Confederate General from Big Sur (1964), about a seemingly delusional man who believes himself to be the descendant of a Confederate general. Brautigan would go on to publish numerous prose and poetry collections until 1982. He committed suicide in 1984.
Richard Aldington (8 July 1892 – 27 July 1962), born Edward Godfree Aldington, was an English writer and poet, and an early associate of the Imagist movement.
He was married to the poet Hilda Doolittle (H. D.) from 1911 to 1938.
Aldington's 50 year career included work in poetry, novels, criticism and biography. He edited The Egoist literary journal and wrote for magazines such as The Times Literary Supplement, Vogue, The Criterion and Poetry. His biography of Wellington (1946) was awarded the James Tait Black Memorial Prize. His circle included writers and critics such as T. S. Eliot, D. H. Lawrence, Ezra Pound, W. B. Yeats, Lawrence Durrell and C. P. Snow. He championed H.D. as the major poetic voice of the Imagist movement and helped to bring her work to international notice.
Robert Browning (7 May 1812 – 12 December 1889) was an English poet and playwright whose mastery of the dramatic monologue made him one of the foremost Victorian poets.
His poems are known for their irony, characterization, dark humour, social commentary, historical settings, and challenging vocabulary and syntax.
Browning's early career began promisingly, but collapsed. The long poems Pauline and Paracelsus received some acclaim, but in 1840 the difficult Sordello, which was seen as wilfully obscure, brought his poetry into disrepute. His reputation took more than a decade to recover, during which time he moved away from the Shelleyan forms of his early period and developed a more personal style.
In 1846, Browning married the older poet Elizabeth Barrett, and went to live in Italy. By the time of her death in 1861, he had published the crucial collection Men and Women. The collection Dramatis Personae and the book-length epic poem The Ring and the Book followed, and made him a leading British poet. He continued to write prolifically, but his reputation today rests largely on the poetry he wrote in this middle period.
When Browning died in 1889, he was regarded as a sage and philosopher-poet who through his writing had made contributions to Victorian social and political discourse. Unusually for a poet, societies for the study of his work were founded while he was still alive. Such Browning Societies remained common in Britain and the United States until the early 20th century.
Robert Herrick (baptised 24 August 1591 – buried 15 October 1674) was a 17th-century English lyric poet and cleric. He is best known for Hesperides, a book of poems. This includes the carpe diem poem "To the Virgins, to Make Much of Time", with the first line "Gather ye rosebuds while ye may".
Robert Louis Stevenson (13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist and travel writer, most noted for Treasure Island, Kidnapped, Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde, and A Child's Garden of Verses.
Born and educated in Edinburgh, Stevenson suffered from serious bronchial trouble for much of his life, but continued to write prolifically and travel widely in defiance of his poor health. As a young man, he mixed in London literary circles, receiving encouragement from Andrew Lang, Edmund Gosse, Leslie Stephen and W. E. Henley, the last of whom may have provided the model for Long John Silver in Treasure Island. Stevenson spent several years in search of a location suited to his health, before finally settling in Samoa, where he died.
A celebrity in his lifetime, Stevenson attracted a more negative critical response for much of the 20th century, though his reputation has been largely restored. He is currently ranked as the 26th most translated author in the world.
Robert Southey (12 August 1774 – 21 March 1843) was an English poet of the Romantic school, one of the Lake Poets along with William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and England's Poet Laureate for 30 years from 1813 until his death in 1843.
Although his fame has been eclipsed by that of Wordsworth and Coleridge, his verse still enjoys some popularity.
Robert Lee Frost (March 26, 1874 – January 29, 1963) was an American poet.
His work was initially published in England before it was published in America. Known for his realistic depictions of rural life and his command of American colloquial speech, Frost frequently wrote about settings from rural life in New England in the early twentieth century, using them to examine complex social and philosophical themes.
Frost was honored frequently during his lifetime and is the only poet to receive four Pulitzer Prizes for Poetry. He became one of America's rare "public literary figures, almost an artistic institution." He was awarded the Congressional Gold Medal in 1960 for his poetic works. On July 22, 1961, Frost was named poet laureate of Vermont.
Sylvia Plath (October 27, 1932 – February 11, 1963) was an American poet, novelist, and short-story writer.
Born in Boston, Massachusetts, she studied at Smith College and Newnham College at the University of Cambridge before receiving acclaim as a poet and writer. She married fellow poet Ted Hughes in 1956, and they lived together in the United States and then in England. They had two children, Frieda and Nicholas, before separating in 1962.
Plath was clinically depressed for most of her adult life, and was treated multiple times with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). She died by suicide in 1963.
Plath is credited with advancing the genre of confessional poetry and is best known for two of her published collections, The Colossus and Other Poems and Ariel, and The Bell Jar, a semi-autobiographical novel published shortly before her death. In 1982, she won a posthumous Pulitzer Prize for The Collected Poems.
Stephen Edwin King (born September 21, 1947) is an American author of horror, supernatural fiction, suspense, and fantasy novels.
His books have sold more than 350 million copies, many of which have been adapted into feature films, miniseries, television series, and comic books. King has published 61 novels (including seven under the pen name Richard Bachman) and six non-fiction books. He has written approximately 200 short stories, most of which have been published in book collections.
King has received Bram Stoker Awards, World Fantasy Awards, and British Fantasy Society Awards. In 2003, the National Book Foundation awarded him the Medal for Distinguished Contribution to American Letters. He has also received awards for his contribution to literature for his entire oeuvre, such as the World Fantasy Award for Life Achievement (2004) and the Grand Master Award from the Mystery Writers of America (2007). In 2015, King was awarded with a National Medal of Arts from the United States National Endowment for the Arts for his contributions to literature. He has been described as the "King of Horror".
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 [OS 7 September] – 13 December 1784), often referred to as Dr. Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, literary critic, biographer, editor, and lexicographer.
He was a devout Anglican. Politically, he was a committed Tory. The Oxford Dictionary of National Biography describes Johnson as "arguably the most distinguished man of letters in English history". He is the subject of James Boswell's The Life of Samuel Johnson, described by Walter Jackson Bate as "the most famous single work of biographical art in the whole of literature".Born in Lichfield, Staffordshire, Johnson attended Pembroke College, Oxford, for just over a year, but a lack of funds forced him to leave. After working as a teacher, he moved to London, where he began to write for The Gentleman's Magazine. His early works include the biography Life of Mr Richard Savage, the poems London and The Vanity of Human Wishes, and the play Irene.
After nine years of work, Johnson's A Dictionary of the English Language was published in 1755. It had a far-reaching effect on Modern English and has been acclaimed as "one of the greatest single achievements of scholarship". This work brought Johnson popularity and success. Until the completion of the Oxford English Dictionary 150 years later, Johnson's was the pre-eminent British dictionary. His later works included essays, an influential annotated edition of The Plays of William Shakespeare, and the widely read tale The History of Rasselas, Prince of Abissinia. In 1763, he befriended James Boswell, with whom he later travelled to Scotland; Johnson described their travels in A Journey to the Western Islands of Scotland. Towards the end of his life, he produced the massive and influential Lives of the Most Eminent English Poets, a collection of biographies and evaluations of 17th- and 18th-century poets.
Johnson was a tall and robust man. His odd gestures and tics were disconcerting to some on first meeting him. Boswell's Life, along with other biographies, documented Johnson's behaviour and mannerisms in such detail that they have informed the posthumous diagnosis of Tourette syndrome, a condition not defined or diagnosed in the 18th century. After a series of illnesses, he died on the evening of 13 December 1784, and was buried in Westminster Abbey. In the years following his death, Johnson began to be recognised as having had a lasting effect on literary criticism, and he was claimed by some to be the only truly great critic of English literature.
Samuel Richardson (baptised 19 August 1689 – 4 July 1761) was an English writer and printer best known for three epistolary novels: Pamela; or, Virtue Rewarded (1740), Clarissa: Or the History of a Young Lady (1748) and The History of Sir Charles Grandison (1753). He printed almost 500 works in his life, including journals and magazines, working periodically with the London bookseller Andrew Millar.
Richardson had been apprenticed to a printer, whose daughter he eventually married. He lost her along with five sons, but remarried and had four daughters who reached adulthood, but no male heirs to continue the print shop. As it ran down, he wrote his first novel at the age of 51 and immediately joined the admired writers of his day. Leading figures he knew included Samuel Johnson and Sarah Fielding, the physicians Behmenist and George Cheyne, and the theologian and writer William Law, whose books he printed. At Law's request, Richardson printed some poems by John Byrom. In literature he rivalled Henry Fielding; the two responded to each other's literary styles.
Thomas Lanier Williams III (March 26, 1911 – February 25, 1983), known by his pen name Tennessee Williams, was an American playwright.
Along with contemporaries Eugene O'Neill and Arthur Miller, he is considered among the three foremost playwrights of 20th-century American drama.After years of obscurity, at age 33 he became suddenly famous with the success of The Glass Menagerie (1944) in New York City. This play closely reflected his own unhappy family background. It was the first of a string of successes, including A Streetcar Named Desire (1947), Cat on a Hot Tin Roof (1955), Sweet Bird of Youth (1959), and The Night of the Iguana (1961). With his later work, he attempted a new style that did not appeal to audiences. His drama A Streetcar Named Desire is often numbered on short lists of the finest American plays of the 20th century alongside Eugene O'Neill's Long Day's Journey into Night and Arthur Miller's Death of a Salesman.Much of Williams' most acclaimed work has been adapted for the cinema. He also wrote short stories, poetry, essays and a volume of memoirs. In 1979, four years before his death, Williams was inducted into the American Theater Hall of Fame.
Theodore Sturgeon (born Edward Hamilton Waldo, February 26, 1918 – May 8, 1985) was an American writer, primarily of fantasy, science fiction and horror.
He was also a critic. He wrote approximately 400 reviews and more than 200 stories.Sturgeon's science fiction novel More Than Human (1953) won the 1954 International Fantasy Award (for SF and fantasy) as the year's best novel and the Science Fiction Writers of America ranked "Baby is Three" number five among the "Greatest Science Fiction Novellas of All Time" to 1964. Ranked by votes for all of their pre-1965 novellas, Sturgeon was second among authors, behind Robert Heinlein.
The Science Fiction and Fantasy Hall of Fame inducted Sturgeon in 2000, its fifth class of two dead and two living writers.
Pierre Jules Théophile Gautier (French: [pjɛʁ ʒyl teofil ɡotje]; 30 August 1811 – 23 October 1872) was a French poet, dramatist, novelist, journalist, and art and literary critic.
While an ardent defender of Romanticism, Gautier's work is difficult to classify and remains a point of reference for many subsequent literary traditions such as Parnassianism, Symbolism, Decadence and Modernism. He was widely esteemed by writers as disparate as Balzac, Baudelaire, the Goncourt brothers, Flaubert, Pound, Eliot, James, Proust and Wilde.
Timothy Francis Leary (October 22, 1920 – May 31, 1996) was an American psychologist and writer known for advocating the exploration of the therapeutic potential of psychedelic drugs under controlled conditions.
As a clinical psychologist at Harvard University, Leary conducted experiments under the Harvard Psilocybin Project in 1960–62 (LSD and psilocybin were still legal in the United States at the time), resulting in the Concord Prison Experiment and the Marsh Chapel Experiment. The scientific legitimacy and ethics of his research were questioned by other Harvard faculty because he took psychedelics together with research subjects and pressured students in his class to take psychedelics in the research studies. Leary and his colleague, Richard Alpert (who later became known as Ram Dass), were fired from Harvard University in May 1963. National illumination as to the effects of psychedelics did not occur until after the Harvard scandal.Leary believed that LSD showed potential for therapeutic use in psychiatry. He used LSD himself and developed a philosophy of mind expansion and personal truth through LSD. After leaving Harvard, he continued to publicly promote the use of psychedelic drugs and became a well-known figure of the counterculture of the 1960s. He popularized catchphrases that promoted his philosophy, such as "turn on, tune in, drop out", "set and setting", and "think for yourself and question authority". He also wrote and spoke frequently about transhumanist concepts involving space migration, intelligence increase, and life extension (SMI²LE), and developed the eight-circuit model of consciousness in his book Exo-Psychology (1977). He gave lectures, occasionally billing himself as a "performing philosopher".During the 1960s and 1970s, he was arrested often enough to see the inside of 36 prisons worldwide. President Richard Nixon once described Leary as "the most dangerous man in America".
Paul Thomas Mann (UK: MAN, US: MAHN; German: [ˈpaʊ̯l ˈtoːmas ˈman]; 6 June 1875 – 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate.
His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novellas are noted for their insight into the psychology of the artist and the intellectual. His analysis and critique of the European and German soul used modernized versions of German and Biblical stories, as well as the ideas of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Friedrich Nietzsche and Arthur Schopenhauer.
Mann was a member of the Hanseatic Mann family and portrayed his family and class in his first novel, Buddenbrooks. His older brother was the radical writer Heinrich Mann and three of Mann's six children, Erika Mann, Klaus Mann and Golo Mann, also became significant German writers. When Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933, Mann fled to Switzerland. When World War II broke out in 1939, he moved to the United States, then returned to Switzerland in 1952. Mann is one of the best-known exponents of the so-called Exilliteratur, German literature written in exile by those who opposed the Hitler regime.
Mann's work influenced many later authors, including Heinrich Böll, Joseph Heller, Yukio Mishima, and Orhan Pamuk.
Thomas Moore (28 May 1779 – 25 February 1852) was an Irish poet, singer, songwriter, and entertainer, now best remembered for the lyrics of "The Minstrel Boy" and "The Last Rose of Summer". As Lord Byron's named literary executor, along with John Murray, Moore was responsible for burning Lord Byron's memoirs after his death.
In his lifetime he was often referred to as Anacreon Moore.From a relatively early age Moore showed an interest in music and other performing arts. He sometimes appeared in musical plays with his friends, such as The Poor Soldier by John O'Keeffe (music by William Shield), and at one point had ambitions to become an actor. Moore attended several Dublin schools including Samuel Whyte's English Grammar School in Grafton Street where he learned the English accent with which he spoke for the rest of his life. In 1795 he graduated from Trinity College, which had recently allowed entry to Catholic students, in an effort to fulfill his mother's dream of his becoming a lawyer. Moore was initially a good student, but he later put less effort into his studies. His time at Trinity came amidst the ongoing turmoil following the French Revolution, and a number of his fellow students such as Robert Emmet were supporters of the United Irishmen movement, although Moore himself never was a member. This movement sought support from the French government to launch a revolution in Ireland. In 1798 a rebellion broke out followed by a French invasion, neither of which succeeded.
Besides Emmet, another formative influence was Edward Hudson, also a fellow student at Trinity College, who played a crucial role in introducing Moore to Edward Bunting's A General Collection of the Ancient Irish Music (1797), later one of the main sources of his own collection of Irish Melodies.
Thomas Stearns Eliot (26 September 1888 – 4 January 1965), "one of the twentieth century's major poets", was also an essayist, publisher, playwright, and literary and social critic.
Born in St. Louis, Missouri to a prominent Boston Brahmin family, he moved to England in 1914 at the age of 25 and would settle, work, and marry there. He became a British subject in 1927 at the age of 39, subsequently renouncing his American passport.Eliot attracted widespread attention for his poem "The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock" (1915), which was seen as a masterpiece of the Modernist movement. It was followed by some of the best-known poems in the English language, including The Waste Land (1922), "The Hollow Men" (1925), "Ash Wednesday" (1930), and Four Quartets (1943). He was also known for his seven plays, particularly Murder in the Cathedral (1935) and The Cocktail Party (1949). He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1948, "for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry".
William E. 'Bill' Vaughan (October 8, 1915 – February 25, 1977) was an American columnist and author.
Born in Saint Louis, Missouri, he wrote a syndicated column for the Kansas City Star from 1946 until his death in 1977. He was published in Reader's Digest and Better Homes and Gardens under the pseudonym Burton Hillis.
His folksy aphorisms (published in his "Starbeams" feature) are often collected in books and on Internet sites.
William Arthur Ward (December 17, 1921–March 30, 1994) was an often quoted writer of inspirational maxims.More than 100 articles, poems and meditations written by Ward were published in such magazines as Reader's Digest, The Phi Delta Kappan, Science of Mind, and various Christian publications.
His column “Pertinent Proverbs” was published by the Fort Worth Star-Telegram and also in American service club publications. He was a frequently quoted writer in Quote, an international weekly digest for public speakers.
A graduate of McMurry College, he received his master's degree at Oklahoma State University but did not complete his doctoral work at the University of Texas and at North Texas State University. In 1962 he was awarded an honorary Oklahoma City University degree in recognition of his “professional achievement, literary contributions and service to others.”
Ward was an assistant to the president of Texas Wesleyan College in Fort Worth beginning in 1955. In addition to his professional responsibilities, he was for two years the director of Methodist men for the Methodist Central Texas Conference, and for four years he taught the 140-member Sigler Bible Class at Polytechnic Methodist Church, where he also served as Sunday School superintendent and a church lay leader.
He was a professional member of the American College Public Relations Association, the International Platform Association, the Religious Public Relations Council and Phi Delta Kappa. In Fort Worth he was on the board of directors of numerous organizations, including Rotary, American Red Cross and Boy Scouts of America.
His biography appears in Who's Who in American Education, Who's Who in Public Relations, and Who's Who in the South and Southwest.
William Seward Burroughs II (February 5, 1914 – August 2, 1997) was an American writer and visual artist.
Burroughs was a primary figure of the Beat Generation and a major postmodernist author whose influence is considered to have affected a range of popular culture as well as literature. Burroughs wrote eighteen novels and novellas, six collections of short stories and four collections of essays. Five books have been published of his interviews and correspondences. He also collaborated on projects and recordings with numerous performers and musicians and made many appearances in films. He was also briefly known by the pen name William Lee. Burroughs created and exhibited thousands of paintings and other visual artworks, including his celebrated 'Gunshot Paintings'.
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker.
Largely unrecognised during his lifetime, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual arts of the Romantic Age. What he called his prophetic works were said by 20th-century critic Northrop Frye to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led 21st-century critic Jonathan Jones to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. While he lived in London his entire life, except for three years spent in Felpham, he produced a diverse and symbolically rich œuvre, which embraced the imagination as "the body of God" or "human existence itself".Although Blake was considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he is held in high regard by later critics for his expressiveness and creativity, and for the philosophical and mystical undercurrents within his work. His paintings and poetry have been characterised as part of the Romantic movement and as "Pre-Romantic". A committed Christian who was hostile to the Church of England (indeed, to almost all forms of organised religion), Blake was influenced by the ideals and ambitions of the French and American Revolutions. Though later he rejected many of these political beliefs, he maintained an amiable relationship with the political activist Thomas Paine; he was also influenced by thinkers such as Emanuel Swedenborg. Despite these known influences, the singularity of Blake's work makes him difficult to classify. The 19th-century scholar William Michael Rossetti characterised him as a "glorious luminary", and "a man not forestalled by predecessors, nor to be classed with contemporaries, nor to be replaced by known or readily surmisable successors".
William Makepeace Thackeray (18 July 1811 – 24 December 1863) was a British novelist, author and illustrator. He is known for his satirical works, particularly Vanity Fair, a panoramic portrait of English society.
William Shakespeare (bapt.
26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English poet, playwright, and actor, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's greatest dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon". His extant works, including collaborations, consist of some 39 plays, 154 sonnets, two long narrative poems, and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright.Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18, he married Anne Hathaway, with whom he had three children: Susanna and twins Hamnet and Judith. Sometime between 1585 and 1592, he began a successful career in London as an actor, writer, and part-owner of a playing company called the Lord Chamberlain's Men, later known as the King's Men. At age 49 (around 1613), he appears to have retired to Stratford, where he died three years later. Few records of Shakespeare's private life survive; this has stimulated considerable speculation about such matters as his physical appearance, his sexuality, his religious beliefs, and whether the works attributed to him were written by others. Such theories are often criticised for failing to adequately note that few records survive of most commoners of the period.
Shakespeare produced most of his known works between 1589 and 1613. His early plays were primarily comedies and histories and are regarded as some of the best work produced in these genres. Until about 1608, he wrote mainly tragedies, among them Hamlet, Othello, King Lear, and Macbeth, all considered to be among the finest works in the English language. In the last phase of his life, he wrote tragicomedies (also known as romances) and collaborated with other playwrights.
Many of Shakespeare's plays were published in editions of varying quality and accuracy in his lifetime. However, in 1623, two fellow actors and friends of Shakespeare's, John Heminges and Henry Condell, published a more definitive text known as the First Folio, a posthumous collected edition of Shakespeare's dramatic works that included all but two of his plays. The volume was prefaced with a poem by Ben Jonson, in which Jonson presciently hails Shakespeare in a now-famous quote as "not of an age, but for all time".Throughout the 20th and 21st centuries, Shakespeare's works have been continually adapted and rediscovered by new movements in scholarship and performance. His plays remain popular and are studied, performed, and reinterpreted through various cultural and political contexts around the world.
Wystan Hugh Auden (21 February 1907 – 29 September 1973) was an English-American poet.
Auden's poetry was noted for its stylistic and technical achievement, its engagement with politics, morals, love, and religion, and its variety in tone, form and content. He is best known for love poems such as "Funeral Blues"; poems on political and social themes such as "September 1, 1939" and "The Shield of Achilles"; poems on cultural and psychological themes such as The Age of Anxiety; and poems on religious themes such as "For the Time Being" and "Horae Canonicae".He was born in York, grew up in and near Birmingham in a professional middle-class family. He attended English independent (or public) schools and studied English at Christ Church, Oxford. After a few months in Berlin in 1928–29, he spent five years (1930–35) teaching in British public schools, then travelled to Iceland and China in order to write books about his journeys.
In 1939 he moved to the United States and became an American citizen in 1946. He taught from 1941 to 1945 in American universities, followed by occasional visiting professorships in the 1950s. From 1947 to 1957 he wintered in New York and summered in Ischia; from 1958 until the end of his life he wintered in New York (in Oxford in 1972–73) and summered in Kirchstetten, Lower Austria.
He came to wide public attention with his first book Poems at the age of twenty-three in 1930; it was followed in 1932 by The Orators. Three plays written in collaboration with Christopher Isherwood between 1935 and 1938 built his reputation as a left-wing political writer. Auden moved to the United States partly to escape this reputation, and his work in the 1940s, including the long poems "For the Time Being" and "The Sea and the Mirror", focused on religious themes. He won the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry for his 1947 long poem The Age of Anxiety, the title of which became a popular phrase describing the modern era. From 1956 to 1961 he was Professor of Poetry at Oxford; his lectures were popular with students and faculty, and served as the basis for his 1962 prose collection The Dyer's Hand.
Auden and Isherwood maintained a lasting but intermittent sexual friendship from around 1927 to 1939, while both had briefer but more intense relations with other men. In 1939, Auden fell in love with Chester Kallman and regarded their relationship as a marriage, but this ended in 1941 when Kallman refused to accept the faithful relations that Auden demanded. However, the two maintained their friendship, and from 1947 until Auden's death they lived in the same house or apartment in a non-sexual relationship, often collaborating on opera libretti such as that of The Rake's Progress, to music by Igor Stravinsky.
Auden was a prolific writer of prose essays and reviews on literary, political, psychological, and religious subjects, and he worked at various times on documentary films, poetic plays, and other forms of performance. Throughout his career he was both controversial and influential, and critical views on his work ranged from sharply dismissive—treating him as a lesser figure than W. B. Yeats and T. S. Eliot—to strongly affirmative, as in Joseph Brodsky's claim that he had "the greatest mind of the twentieth century". After his death, his poems became known to a much wider public than during his lifetime through films, broadcasts, and popular media.
Federico del Sagrado Corazón de Jesús García Lorca (Spanish pronunciation: [feðeˈɾiko ðel saˈɣɾaðo koɾaˈθon de xeˈsuz ɣaɾˈθi.a ˈloɾka]; 5 June 1898 – 19 August 1936), known as Federico García Lorca (English: gar-SEE-ə LOR-kə), was a Spanish poet, playwright, and theatre director.
García Lorca achieved international recognition as an emblematic member of the Generation of '27, a group consisting of mostly poets who introduced the tenets of European movements (such as symbolism, futurism, and surrealism) into Spanish literature. He was executed by Rebel faction forces at the beginning of the Spanish Civil War. His body or bones have never been found.
Fyodor Dostoevsky, in full Fyodor Mikhaylovich Dostoyevsky, Russian novelist and short-story writer whose psychological penetration into the darkest recesses of the human heart, together with his unsurpassed moments of illumination, had an immense influence on 20th-century fiction.
François Villon (pronounced [fʁɑ̃swa vijɔ̃] in modern French; in fifteenth-century French, [frɑnswɛ vilɔn], c. 1431 – c. 1463) is the best known French poet of the Late Middle Ages.
A ne'er-do-well who was involved in criminal behavior and had multiple encounters with law enforcement authorities, Villon wrote about some of these experiences in his poems.
Francis Scott Key Fitzgerald (September 24, 1896 – December 21, 1940) was an American fiction writer, whose works helped to illustrate the flamboyance and excess of the Jazz Age.
While he achieved popular success, fame, and fortune in his lifetime, he did not receive much critical acclaim until after his death. Perhaps the most notable member of the "Lost Generation" of the 1920s, Fitzgerald is now widely regarded as one of the greatest American writers of the 20th century. He finished four novels: This Side of Paradise, The Beautiful and Damned, The Great Gatsby, and Tender Is the Night. A fifth, unfinished novel, The Last Tycoon, was published posthumously. Four collections of his short stories were published, as well as 164 short stories in magazines during his lifetime.
Fulke Greville, 1st Baron Brooke, de jure 13th Baron Latimer and 5th Baron Willoughby de Broke KB PC, known before 1621 as Sir Fulke Greville, was an Elizabethan poet, dramatist, and statesman who sat in the House of Commons at various times between 1581 and 1621, when he was raised to the peerage.
Hunter Stockton Thompson (July 18, 1937 – February 20, 2005) was an American journalist and author, and the founder of the gonzo journalism movement.
He first rose to prominence with the publication of Hell's Angels (1967), a book for which he spent a year living and riding with the Hells Angels motorcycle gang in order to write a first-hand account of the lives and experiences of its members.
In 1970, he wrote an unconventional magazine feature titled "The Kentucky Derby Is Decadent and Depraved" for Scanlan's Monthly which both raised his profile and established him as a writer with counterculture credibility. It also set him on a path to establishing his own sub-genre of New Journalism which he called "Gonzo," which was essentially an ongoing experiment in which the writer becomes a central figure and even a participant in the events of the narrative.
Thompson remains best known for Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas (1971), a book first serialized in Rolling Stone in which he grapples with the implications of what he considered the failure of the 1960s counterculture movement. It was adapted on film twice: loosely in Where the Buffalo Roam starring Bill Murray as Thompson in 1980, and directly in 1998 by director Terry Gilliam in a film starring Johnny Depp and Benicio del Toro. The Doonesbury cartoon character Duke – who was modeled after Thompson – pens an essay about "my shoplifting conviction" titled "Fear and Loathing at Macy's Menswear", a reference to Thompson's book.
Politically minded, Thompson ran unsuccessfully for sheriff of Pitkin County, Colorado in 1970 on the Freak Power ticket. He became well known for his dislike of Richard Nixon, who he claimed represented "that dark, venal, and incurably violent side of the American character". He covered Nixon's 1972 reelection campaign for Rolling Stone and later collected the stories in book form as Fear and Loathing on the Campaign Trail '72.
Thompson's output notably declined from the mid-1970s, as he struggled with the consequences of fame, and he complained that he could no longer merely report on events as he was too easily recognized. He was also known for his lifelong use of alcohol and illegal narcotics, his love of firearms, and his iconoclastic contempt for authoritarianism. He often remarked: "I hate to advocate drugs, alcohol, violence, or insanity to anyone, but they've always worked for me."
Thompson committed suicide at the age of 67, following a series of health problems. In accordance with his wishes, his ashes were fired out of a cannon in a ceremony funded by his friend Johnny Depp and attended by friends including then-Senator John Kerry and Jack Nicholson. Hari Kunzru wrote that "the true voice of Thompson is revealed to be that of American moralist ... one who often makes himself ugly to expose the ugliness he sees around him."
Helen Adams Keller (June 27, 1880 – June 1, 1968) was an American author, political activist, and lecturer.
She was the first deaf-blind person to earn a Bachelor of Arts degree. The story of Keller and her teacher, Anne Sullivan, was made famous by Keller's autobiography, The Story of My Life, and its adaptations for film and stage, The Miracle Worker. Her birthplace in West Tuscumbia, Alabama, is now a museum and sponsors an annual "Helen Keller Day". Her June 27 birthday is commemorated as Helen Keller Day in Pennsylvania and, in the centenary year of her birth, was recognized by a presidential proclamation from Jimmy Carter.
A prolific author, Keller was well-traveled and outspoken in her convictions. A member of the Socialist Party of America and the Industrial Workers of the World, she campaigned for women's suffrage, labor rights, socialism, antimilitarism, and other similar causes. She was inducted into the Alabama Women's Hall of Fame in 1971 and was one of twelve inaugural inductees to the Alabama Writers Hall of Fame on June 8, 2015.
Henry Charles Bukowski (born Heinrich Karl Bukowski; August 16, 1920 – March 9, 1994) was a German-American poet, novelist, and short story writer.
His writing was influenced by the social, cultural, and economic ambiance of his home city of Los Angeles. His work addresses the ordinary lives of poor
Americans, the act of writing, alcohol, relationships with women, and the drudgery of work. Bukowski wrote thousands of poems, hundreds of short stories and six novels, eventually publishing over 60 books. The FBI kept a file on him as a result of his column Notes of a Dirty Old Man in the LA underground newspaper Open City.Bukowski published extensively in small literary magazines and with small presses beginning in the early 1940s and continuing on through the early 1990s. As noted by one reviewer, "Bukowski continued to be, thanks to his antics and deliberate clownish performances, the king of the underground and the epitome of the littles in the ensuing decades, stressing his loyalty to those small press editors who had first championed his work and consolidating his presence in new ventures such as the New York Quarterly, Chiron Review, or Slipstream." Some of these works include his Poems Written Before Jumping Out of an 8 Story Window, published by his friend and fellow poet Charles Potts, and better known works such as Burning in Water, Drowning in Flame. These poems and stories were later republished by John Martin's Black Sparrow Press (now HarperCollins/Ecco Press) as collected volumes of his work.
In 1986 Time called Bukowski a "laureate of American lowlife". Regarding Bukowski's enduring popular appeal, Adam Kirsch of The New Yorker wrote, "the secret of Bukowski's appeal ... [is that] he combines the confessional poet's promise of intimacy with the larger-than-life aplomb of a pulp-fiction hero."Since his death in 1994, Bukowski has been the subject of a number of critical articles and books about both his life and writings, despite his work having received relatively little attention from academic critics in America during his lifetime. In contrast, Bukowski enjoyed extraordinary fame in Europe, especially in Germany, the place of his birth.
Charles John Huffam Dickens (7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic.
He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian era. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime, and by the 20th century critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are still widely read today.
Charles Kingsley (12 June 1819 – 23 January 1875) was a broad church priest of the Church of England, a university professor, social reformer, historian, novelist and poet.
He is particularly associated with Christian socialism, the working men's college, and forming labour cooperatives, which failed, but encouraged later working reforms. He was a friend and correspondent of Charles Darwin.
Charles Mackay (27 March 1814 – 24 December 1889) was a Scottish poet, journalist, author, anthologist, novelist, and songwriter, remembered mainly for his book Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds.
Charles Pierre Baudelaire (UK: , US: ; French: [ʃaʁl bodlɛʁ] (listen); 9 April 1821 – 31 August 1867) was a French poet who also produced notable work as an essayist, art critic, and pioneering translator of Edgar Allan Poe.
His most famous work, a book of lyric poetry titled Les Fleurs du mal (The Flowers of Evil), expresses the changing nature of beauty in the rapidly industrializing Paris during the mid-19th century. Baudelaire's highly original style of prose-poetry influenced a whole generation of poets including Paul Verlaine, Arthur Rimbaud and Stéphane Mallarmé, among many others. He is credited with coining the term "modernity" (modernité) to designate the fleeting, ephemeral experience of life in an urban metropolis, and the responsibility of artistic expression to capture that experience.
Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros (October 1, 1842 – August 9, 1888) was a French poet and inventor.
He was born in Fabrezan, Aude.
Cros was a well-regarded poet and humorous writer. As an inventor, he was interested in the fields of transmitting graphics by telegraph and making photographs in color, but he is perhaps best known for being the first person to conceive a method for reproducing recorded sound, an invention he named the Paleophone.
Charles Cros died in Paris at the age of 45.
Edward Estlin "E. E." Cummings (October 14, 1894 – September 3, 1962), often styled as "e e cummings", as he is attributed in many of his published works, was an American poet, painter, essayist, author, and playwright.
He wrote approximately 2,900 poems, two autobiographical novels, four plays, and several essays. He is often regarded as one of the most important American poets of the 20th century.
Cummings is associated with modernist free-form poetry. Much of his work has idiosyncratic syntax and uses lower case spellings for poetic expression. His use of lower case extended to rendering even the personal pronoun I as i, as in the phrase "i shall go.”
Edgar Allan Poe (born Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, editor, and literary critic.
Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is widely regarded as a central figure of Romanticism in the United States and of American literature as a whole, and he was one of the country's earliest practitioners of the short story. He is generally considered the inventor of the detective fiction genre and is further credited with contributing to the emerging genre of science fiction. He was the first well-known American writer to earn a living through writing alone, resulting in a financially difficult life and career.Poe was born in Boston, the second child of actors David and Elizabeth "Eliza" Arnold Hopkins Poe. His father abandoned the family in 1810, and his mother died the following year. Thus orphaned, the child was taken in by John and Frances Allan of Richmond, Virginia. They never formally adopted him, but he was with them well into young adulthood. Tension developed later as John Allan and Edgar Poe repeatedly clashed over debts, including those incurred by gambling, and the cost of Poe's secondary education. He attended the University of Virginia but left after a year due to lack of money. Edgar Poe quarreled with John Allan over the funds for his education and enlisted in the Army in 1827 under an assumed name. It was at this time that his publishing career began with the anonymous collection Tamerlane and Other Poems (1827), credited only to "a Bostonian". Edgar Poe and John Allan reached a temporary rapprochement after the death of Frances Allan in 1829. Poe later failed as an officer cadet at West Point, declaring a firm wish to be a poet and writer, and he ultimately parted ways with John Allan.
Poe switched his focus to prose and spent the next several years working for literary journals and periodicals, becoming known for his own style of literary criticism. His work forced him to move among several cities, including Baltimore, Philadelphia, and New York City. He married his 13-year-old cousin, Virginia Clemm, in 1836. In January 1845, Poe published his poem "The Raven" to instant success, but Virginia died of tuberculosis two years after its publication.
Poe planned for years to produce his own journal The Penn (later renamed The Stylus), but he died before it could be produced. He died in Baltimore on October 7, 1849, at age 40; the cause of his death is unknown and has been variously attributed to alcohol, "brain congestion", cholera, drugs, heart disease, rabies, suicide, tuberculosis, and other causes.Poe and his works influenced literature around the world, as well as specialized fields such as cosmology and cryptography. He and his work appear throughout popular culture in literature, music, films, and television. A number of his homes are dedicated museums today. The Mystery Writers of America present an annual award known as the Edgar Award for distinguished work in the mystery genre.
Aesop ( EE-sop; Greek: Αἴσωπος, Aisōpos; c. 620 – 564 BCE) was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as Aesop's Fables.
Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous tales credited to him were gathered across the centuries and in many languages in a storytelling tradition that continues to this day. Many of the tales are characterized by animals and inanimate objects that speak, solve problems, and generally have human characteristics.
Scattered details of Aesop's life can be found in ancient sources, including Aristotle, Herodotus, and Plutarch. An ancient literary work called The Aesop Romance tells an episodic, probably highly fictional version of his life, including the traditional description of him as a strikingly ugly slave (δοῦλος) who by his cleverness acquires freedom and becomes an adviser to kings and city-states. Older spellings of his name have included Esop(e) and Isope. Depictions of Aesop in popular culture over the last 2500 years have included many works of art and his appearance as a character in numerous books, films, plays, and television programs.
Elbert Green Hubbard was an American writer, publisher, artist, and philosopher.
Ella Wheeler Wilcox (November 5, 1850 – October 30, 1919) was an American author and poet.
Her works include Poems of Passion and Solitude, which contains the lines "Laugh, and the world laughs with you; weep, and you weep alone". Her autobiography, The Worlds and I, was published in 1918, a year before her death.
Emily Jane Brontë (30 July 1818 – 19 December 1848) was an English novelist and poet who is best known for her only novel, Wuthering Heights, now considered a classic of English literature.
Emily was the third-eldest of the four surviving Brontë siblings, between the youngest Anne and her brother Branwell. She published under the pen name Ellis Bell.
Emily Elizabeth Dickinson (December 10, 1830 – May 15, 1886) was an American poet.
Dickinson was born in Amherst, Massachusetts, into a prominent family with strong ties to its community. After studying at the Amherst Academy for seven years in her youth, she briefly attended the Mount Holyoke Female Seminary before returning to her family's house in Amherst.
Evidence suggests that Dickinson lived much of her life in isolation. Considered an eccentric by locals, she developed a penchant for white clothing and was known for her reluctance to greet guests or, later in life, to even leave her bedroom. Dickinson never married, and most friendships between her and others depended entirely upon correspondence.While Dickinson was a prolific poet, fewer than a dozen of her nearly 1,800 poems were published during her lifetime. The poems published then were usually edited significantly to fit conventional poetic rules. Her poems were unique to her era. They contain short lines, typically lack titles, and often use slant rhyme as well as unconventional capitalization and punctuation. Many of her poems deal with themes of death and immortality, two recurring topics in letters to her friends.
Although Dickinson's acquaintances were likely aware of her writing, it was not until after her death in 1886—when Lavinia, Dickinson's younger sister, discovered her cache of poems—that the breadth of her work became public. Her first collection of poetry was published in 1890 by personal acquaintances Thomas Wentworth Higginson and Mabel Loomis Todd, though both heavily edited the content. A 1998 New York Times article revealed that of the many edits made to Dickinson's work, the name "Susan" was often deliberately removed. At least eleven of Dickinson's poems were dedicated to sister-in-law Susan Huntington Gilbert Dickinson, though all the dedications were obliterated, presumably by Todd. A complete, and mostly unaltered, collection of her poetry became available for the first time when scholar Thomas H. Johnson published The Poems of Emily Dickinson in 1955.
Émile Adolphe Gustave Verhaere was a Belgian poet and art critic who wrote in the French language. He was one of the founders of the school of Symbolism and was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature on six occasions.
Andrew Marvell (31 March 1621 – 16 August 1678) was an English metaphysical poet, satirist and politician who sat in the House of Commons at various times between 1659 and 1678.
During the Commonwealth period he was a colleague and friend of John Milton. His poems range from the love-song "To His Coy Mistress", to evocations of an aristocratic country house and garden in "Upon Appleton House" and "The Garden", the political address "An Horatian Ode upon Cromwell's Return from Ireland", and the later personal and political satires "Flecknoe" and "The Character of Holland".
John Anthony Burgess Wilson, (25 February 1917 – 22 November 1993), who published under the name Anthony Burgess, was an English writer and composer.
Although Burgess was predominantly a comic writer, his dystopian satire A Clockwork Orange remains his best-known novel. In 1971, it was adapted into a highly controversial film by Stanley Kubrick, which Burgess said was chiefly responsible for the popularity of the book. Burgess produced numerous other novels, including the Enderby quartet, and Earthly Powers. He wrote librettos and screenplays, including the 1977 TV mini-series Jesus of Nazareth. He worked as a literary critic for several publications, including The Observer and The Guardian, and wrote studies of classic writers, notably James Joyce. A versatile linguist, Burgess lectured in phonetics, and translated Cyrano de Bergerac, Oedipus Rex, and the opera Carmen, among others.
Burgess also composed over 250 musical works; he considered himself as much a composer as an author, although he enjoyed considerably more success in writing.
Anthony Jay Robbins (born Anthony J. Mahavoric; February 29, 1960) is an American author, philanthropist, and life coach.
Robbins is known for his infomercials, seminars, and self-help books including Unlimited Power and Awaken the Giant Within.
In 2015 and 2016 Robbins was listed on the Worth Magazine Power 100 list. His seminars are organized through Robbins Research International.
Ernest Christopher Dowson (2 August 1867 – 23 February 1900) was an English poet, novelist, short-story writer, often associated with the Decadent movement.
Ernest Miller Hemingway (July 21, 1899 – July 2, 1961) was an American journalist, novelist, short-story writer, and sportsman.
His economical and understated style—which he termed the iceberg theory—had a strong influence on 20th-century fiction, while his adventurous lifestyle and his public image brought him admiration from later generations. Hemingway produced most of his work between the mid-1920s and the mid-1950s, and he won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1954. He published seven novels, six short-story collections, and two non-fiction works. Three of his novels, four short-story collections, and three non-fiction works were published posthumously. Many of his works are considered classics of American literature.
Hemingway was raised in Oak Park, Illinois. After high school, he was a reporter for a few months for The Kansas City Star before leaving for the Italian Front to enlist as an ambulance driver in World War I. In 1918, he was seriously wounded and returned home. His wartime experiences formed the basis for his novel A Farewell to Arms (1929).
In 1921, Hemingway married Hadley Richardson, the first of four wives. They moved to Paris where he worked as a foreign correspondent and fell under the influence of the modernist writers and artists of the 1920s' "Lost Generation" expatriate community. His debut novel The Sun Also Rises was published in 1926. He divorced Richardson in 1927 and married Pauline Pfeiffer; they divorced after he returned from the Spanish Civil War, where he had been a journalist. He based For Whom the Bell Tolls (1940) on his experience there. Martha Gellhorn became his third wife in 1940; they separated after he met Mary Welsh in London during World War II. He was present with the troops as a journalist at the Normandy landings and the liberation of Paris.
Hemingway went on safari to Africa shortly after the publication of The Old Man and the Sea (1952), where he was involved in two successive near-fatal plane crashes that left him in pain and ill-health for much of the rest of his life. In 1959, he bought a house in Ketchum, Idaho where he ended his own life in mid-1961.
Ian Lancaster Fleming (28 May 1908 – 12 August 1964) was an English author, journalist and naval intelligence officer who is best known for his James Bond series of spy novels.
Fleming came from a wealthy family connected to the merchant bank Robert Fleming & Co., and his father was the Member of Parliament for Henley from 1910 until his death on the Western Front in 1917. Educated at Eton, Sandhurst and, briefly, the universities of Munich and Geneva, Fleming moved through several jobs before he started writing.
While working for Britain's Naval Intelligence Division during the Second World War, Fleming was involved in planning Operation Goldeneye and in the planning and oversight of two intelligence units, 30 Assault Unit and T-Force. His wartime service and his career as a journalist provided much of the background, detail and depth of the James Bond novels.
Fleming wrote his first Bond novel, Casino Royale, in 1952. It was a success, with three print runs being commissioned to cope with the demand. Eleven Bond novels and two collections of short stories followed between 1953 and 1966. The novels revolve around James Bond, an officer in the Secret Intelligence Service, commonly known as MI6. Bond is also known by his code number, 007, and was a commander in the Royal Naval Reserve. The Bond stories rank among the best-selling series of fictional books of all time, having sold over 100 million copies worldwide. Fleming also wrote the children's story Chitty-Chitty-Bang-Bang and two works of non-fiction. In 2008, The Times ranked Fleming 14th on its list of "The 50 greatest British writers since 1945".
Fleming was married to Ann Charteris, who was divorced from the second Viscount Rothermere because of her affair with the author. Fleming and Charteris had a son, Caspar. Fleming was a heavy smoker and drinker for most of his life and succumbed to heart disease in 1964 at the age of 56. Two of his James Bond books were published posthumously; other writers have since produced Bond novels. Fleming's creation has appeared in film twenty-six times, portrayed by seven actors.
Janusz Leon Wiśniewski (born 18 August 1954 in Toruń) is a Polish scientist and writer mostly known for his novel S@motność w Sieci translated into English as Loneliness on the Net[1].
Wiśniewski holds a Master in Physics and Master in Economics, both qualifications obtained from Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, PhD in Information Technology from Warsaw University of Technology and Habilitation in Chemistry from the Technical University of Łódź. He is one of the authors of the computer program AutoNom, a naming tool for organic substances in the IUPAC nomenclature [2]. Currently Wiśniewski lives and works in Frankfurt, Germany. Apart from his native Polish, he is also fluent in German, English and Russian.
His most famous novel S@motność w Sieci (Loneliness on the Net) was published in 2001 and translated into many languages. There is a popular Polish film based on the novel.
- quotations /
- quotes by Famous People /
- Quotes by writers and poets